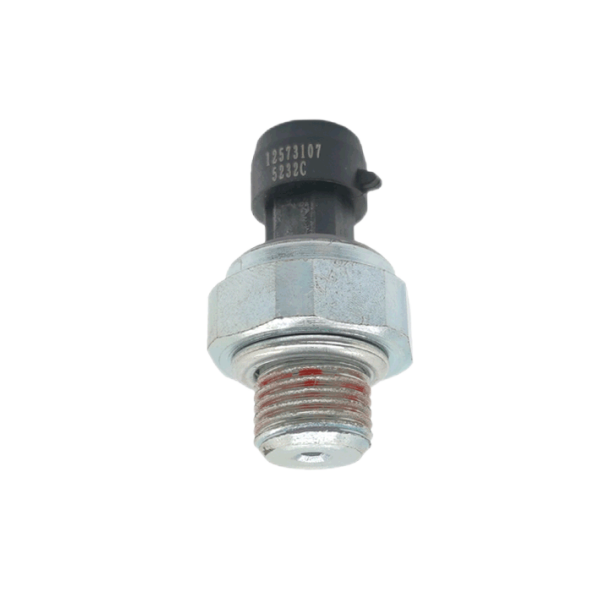
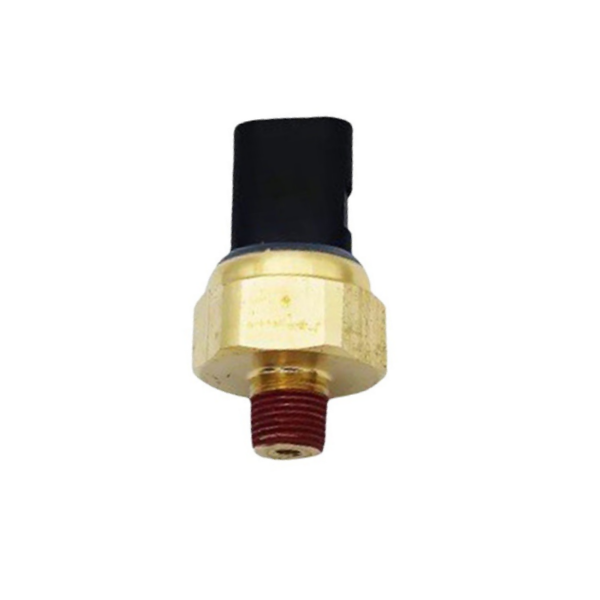
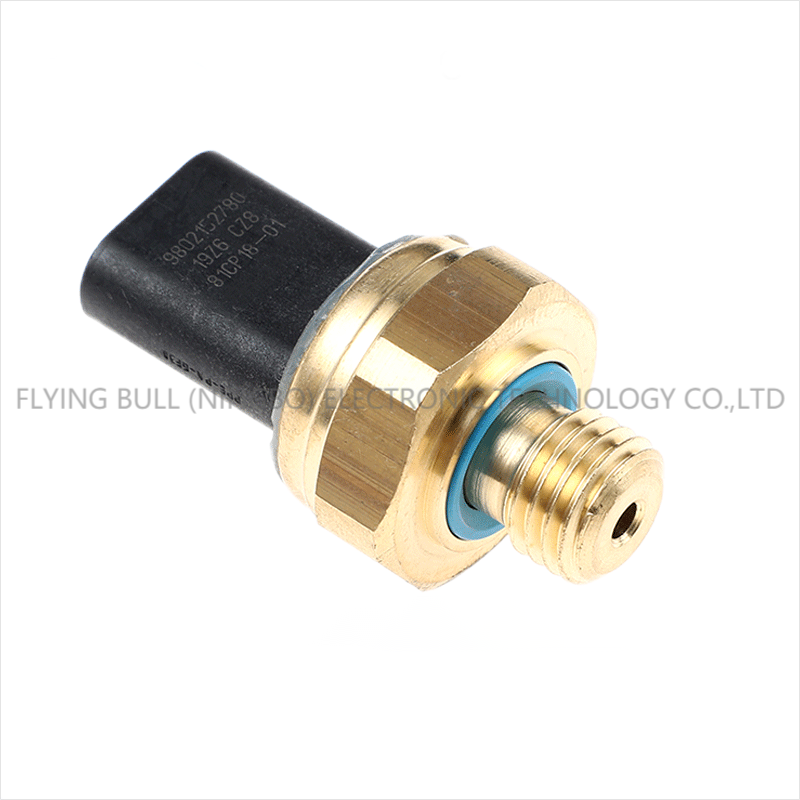
Oil pressure sensor for construction machinery 12617592532
Product introduction
Sensor characteristics
A sensor refers to a device or device that can sense a specified physical quantity and convert it into a usable input signal according to a certain law. Simply put, a sensor is a device that converts non-electric quantity into electric quantity.
A sensor usually consists of three parts: a sensitive element, a conversion element and a measuring circuit.
1), the sensitive element refers to the part that can directly feel (or respond to) the measured, that is, the sensitive element that is measured through the sensor is converted into a non-electric quantity or other quantity that has a definite relationship with the measured.
2) The conversion element converts the non-electric quantity into an electric parameter.
Static characteristic parameter index of sensor
1. Sensitivity
Sensitivity refers to the ratio of output Y to input X of the sensor at steady state, or the ratio of increment of output Y to increment of input X, which is expressed by k as
k=dY/dX
2. Resolution
The minimum change that a sensor can detect within a specified measurement range is called resolution.
3. Measuring range and measuring range
Within the allowable error limit, the range from the lower limit to the upper limit of the measured value is called the measuring range.
4. Linearity (nonlinear error)
Under specified conditions, the percentage of the maximum deviation between the sensor calibration curve and the fitted straight line and the full-scale output value is called linearity or nonlinear error.
5. Hysteresis
Hysteresis refers to the degree of inconsistency between the positive stroke characteristics and the reverse stroke characteristics of the sensor under the same working conditions.
6. Repeatability
Repeatability refers to the inconsistency of the characteristic curve obtained by continuously changing the input quantity in the same direction for many times in the whole measuring range under the same working conditions.
⒎ Zero drift and temperature drift
When the sensor has no input or the input is another value, the percentage of the maximum deviation of the input value from the original indication value and the full scale is zero drift at regular intervals. However, for every 1℃ increase in temperature, the percentage of the maximum deviation of the sensor output value to the full scale is called temperature drift.
Product picture

Company details







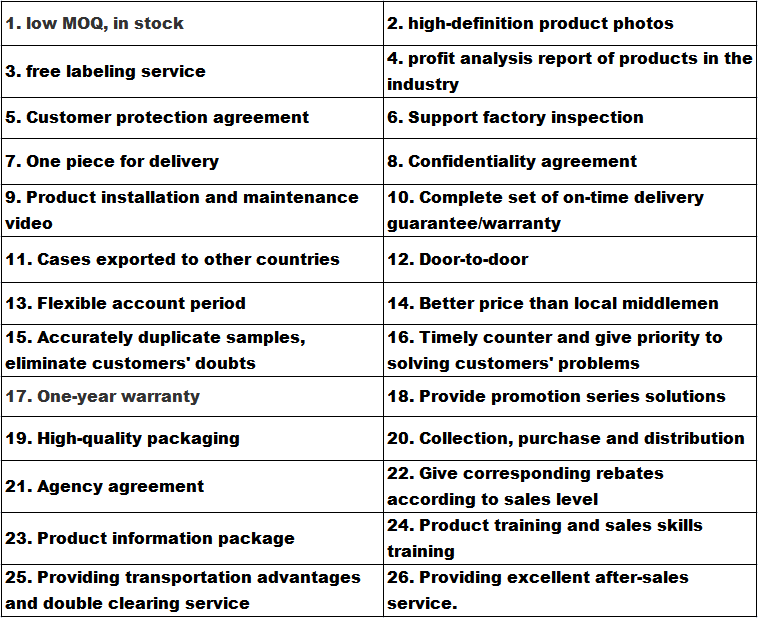
Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ














