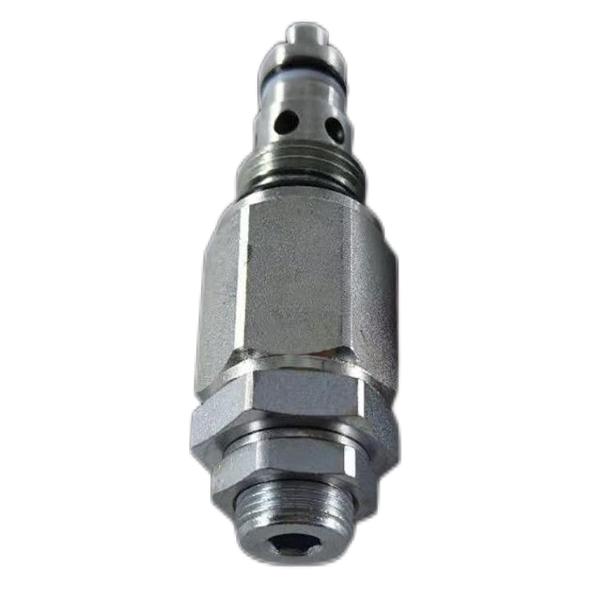
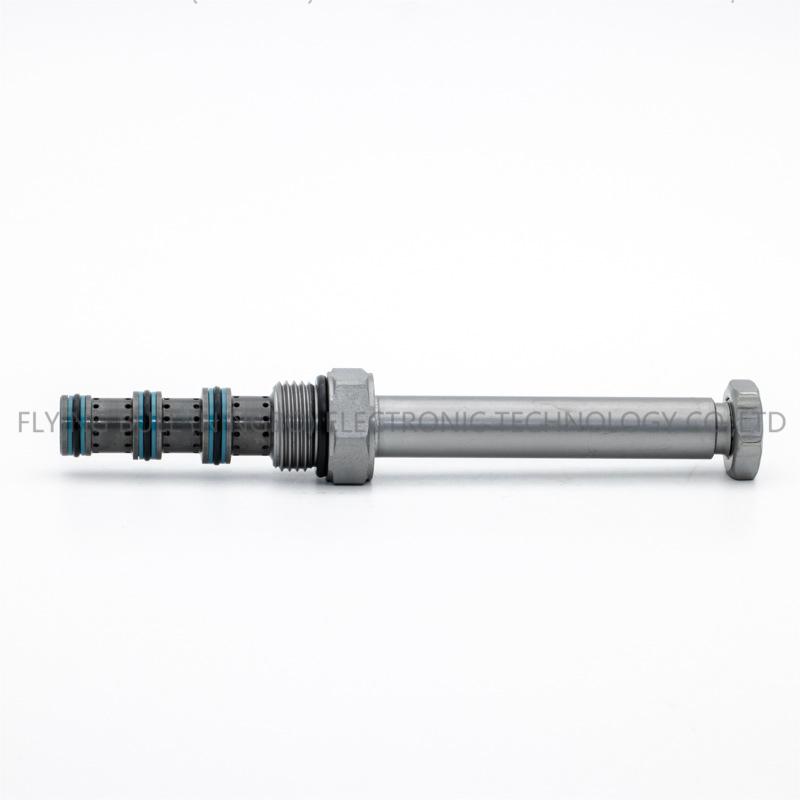
Three-position four-way N-type reversing valve SV08-47B
Details
Temperature environment:normal atmospheric temperature
Flow direction:commutate
Optional accessories:coil
Applicable industries:machinery
Type of drive:electromagnetism
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
Three-position four-way electromagnetic directional valve is a new product developed for G series forklift trucks, and has obtained national patent. It is an essential component for electro-hydraulic reversing of all kinds of forklifts. In order to ensure the quality, the ex-factory test standard of solenoid valve is completely in accordance with international standards: under the harsh conditions of oil temperature of 130 degrees and rated voltage of minus 15%, it meets the performance requirements.
Three-position four-way electromagnetic directional valve has three disadvantages, such as large volume, poor anti-vibration and waterproof performance, and its application environment is greatly limited. The new three-position four-way electromagnetic directional valve has made great improvements in structural design, process design and material selection. Compared with the traditional solenoid valve, the volume is reduced by 1/3, and it has strong shockproof and waterproof performance.
Advantage
Accurate action, high degree of automation, stable and reliable work, but it needs to be attached with a driving and cooling system, and its structure is more complicated; The disc structure is simple, and it is mostly used in the production process with small flow.
In petroleum, chemical, mining and metallurgical industries, the six-way reversing valve is an important fluid reversing device. The valve is installed in the pipeline conveying lubricating oil in the thin oil lubrication system. By changing the relative position of the sealing assembly in the valve body, the channels of the valve body are connected or disconnected, so as to control the reversing and start-stop of the fluid.
Classify
(1) Motor directional control valve, also known as travel valve.
(2) Electromagnetic directional valve, which is a directional control valve that uses electromagnetic attraction to control the transposition of the valve core.
(3) Electro-hydraulic directional valve, which is a compound valve composed of electromagnetic directional valve and hydraulic directional valve.
(4) Manual directional control valve, which is a directional control valve that uses a manual push lever to manipulate the spool transposition.
Product specification

Company details







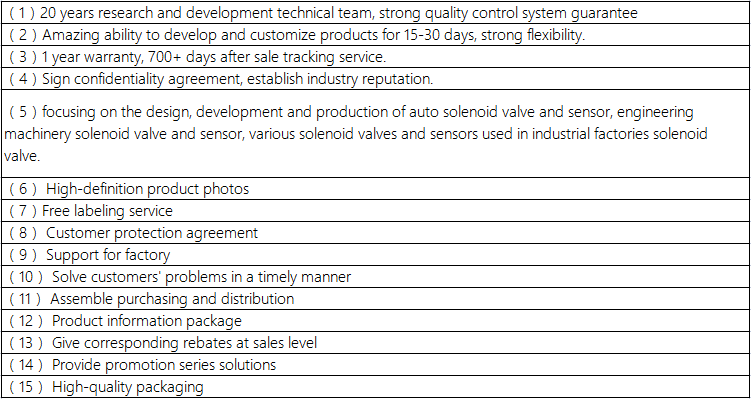
Company advantage
Transportation

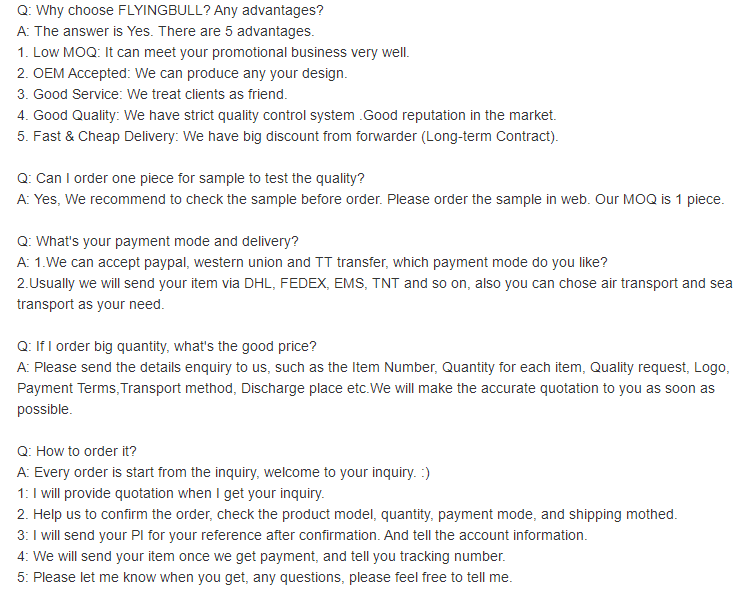
FAQ