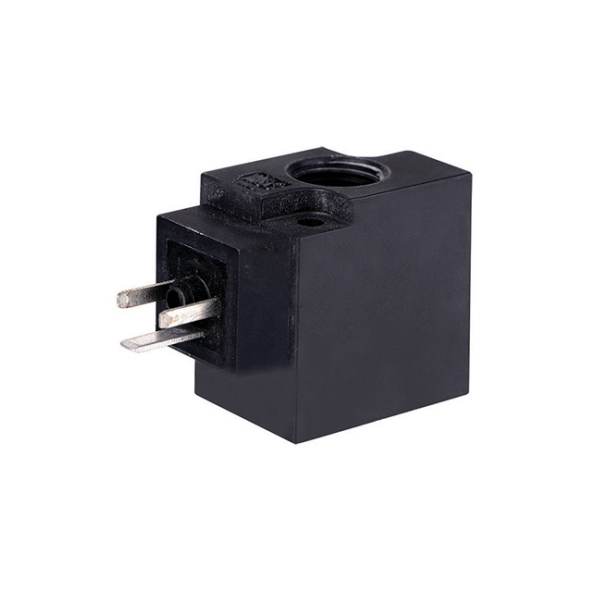
Thermosetting plastic package electromagnetic coil QVT306
Details
Applicable Industries: Building Material Shops, Machinery Repair Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Farms, Retail, Construction works , Advertising Company
Product name: Solenoid coil
Normal Voltage: RAC220V RDC110V DC24V
Normal Power (RAC): 4W
Normal Power (DC): 5.7W
Insulation Class: H
Connection Type: 2×0.8
Other special voltage: Customizable
Other special power: Customizable
Product No.: SB867
Product Type: QVT306
Supply Ability
Selling Units: Single item
Single package size: 7X4X5 cm
Single gross weight: 0.300 kg
Product introduction
What are the aspects of inductance parameters?
1. Quality factor quality factor:
Quality factor Q is a factor used to measure the relationship between the energy stored by energy storage elements (inductors or capacitors) and their energy consumption, which is expressed as: Q=2π maximum stored energy/weekly energy loss. Generally speaking, the larger the Q value of the inductance coil, the better, but too large will make the stability of the working circuit worse.
2, the Inductance:
When the current in a coil changes, the magnetic flux passing through the coil loop itself caused by the changed current also changes, causing the coil itself to induce electromotive force. Self-inductance coefficient is a physical quantity that represents the self-inductance ability of a coil. It is also called self-inductance or inductance. It is expressed by L. Taking Henry (H) as the unit, one thousandth of it is called millihenh (mH), one millionth is called millihenh (H), and one thousandth of it is called Nahen (NH).
3. DC Resistance(DCR):
In inductance planning, the smaller the DC resistance, the better. The measuring unit is ohm, which is generally marked by its maximum value.
4, the Self-resonant frequency:
Inductor is not a purely inductive element, but also has the weight of distributed capacitance. The resonance at a certain frequency caused by the inherent inductance and distributed capacitance of inductor itself is called self-harmonic frequency, also known as resonance frequency. Expressed in S.R.F, the unit is megahertz (MHz).
5. Impedance value:
The impedance value of an inductor refers to the sum of all its impedances under current (complex number), including the communication and DC parts. The impedance value of the DC part is only the DC resistance of the winding (real part), and the impedance value of the communication part includes the reactance (imaginary part) of the inductor. In this sense, the inductor can also be regarded as a "communication resistor". 6. Rated current: The continuous DC current intensity that can pass through an inductor is allowed. The DC current intensity is based on the maximum temperature rise of the inductor in the maximum additional ambient temperature. The extra current is related to the ability of an inductor to reduce the loss of winding by low DC resistance, and also related to the ability of the inductor to dissipate the loss of winding energy. Therefore, the extra current can be improved by reducing the DC resistance or increasing the inductance scale. For low-frequency current waveforms, its root mean square current value
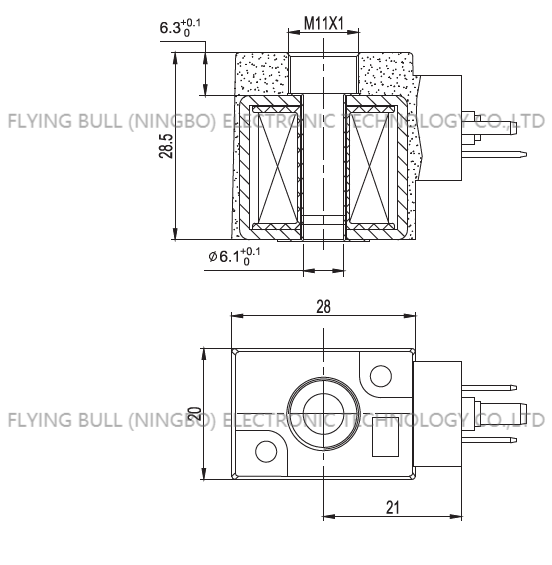
Product picture
Company details







Company advantage

Transportation

FAQ












