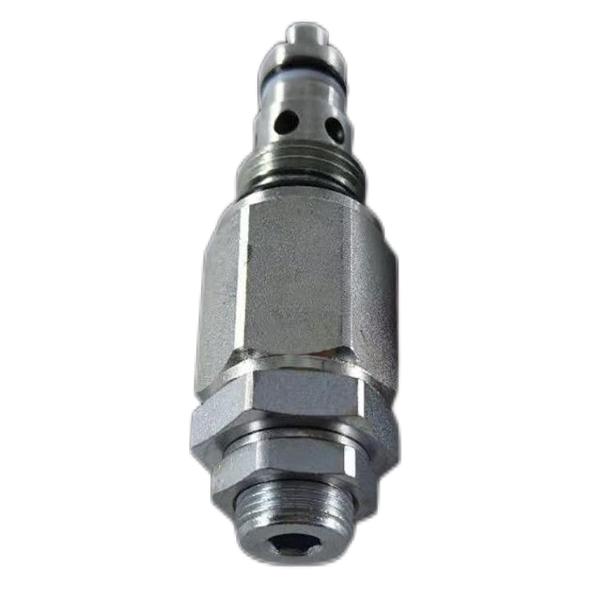
Suitable for CAT Carter 313 346-4995 proportional solenoid valves
Details
Sealing material:Direct machining of valve body
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories:valve body
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
The purpose of the relief valve
Constant pressure overflow effect: In the quantitative pump throttling regulation system, the quantitative pump provides a constant flow rate. When the system pressure increases, the flow demand will decrease. At this time, the relief valve is opened, so that the excess flow flows back to the tank, to ensure that the relief valve inlet pressure, that is, the pump outlet pressure is constant (the valve port is often opened with pressure fluctuations).
Safety protection: When the system is working normally, the valve is closed. Only when the load exceeds the specified limit (system pressure exceeds the set pressure), the overflow is turned on for overload protection, so that the system pressure is no longer increased (usually the set pressure of the relief valve is 10% to 20% higher than the maximum working pressure of the system).
Used as a unloading valve
Act as a remote pressure regulator
High and low pressure multistage control valve
Acting sequence valve
For generating back pressure (string on return circuit)
Taper valve type direct acting relief valve
Taper valve type direct acting relief valve
Taper valve type direct acting relief valve. The left end of the taper valve is provided with a bias disk to hold the pressure spring, and the right end of the taper valve is provided with a damping piston (on the one hand, the damping piston plays a damping role when the taper valve is opened or closed, which is used to improve the stability of the taper valve; On the other hand, it is used to ensure that the poppet valve will not tilt after opening. The imported pressure oil (pressure P) can enter the bottom of the piston through the radial clearance of the piston, forming A left liquid pressure F=P·A (A is the bottom area of the piston). When the liquid pressure F acting on the bottom is greater than the spring force, the cone valve port opens, and the oil spills back to the tank through the cone valve port. As soon as the port is open,
Product specification
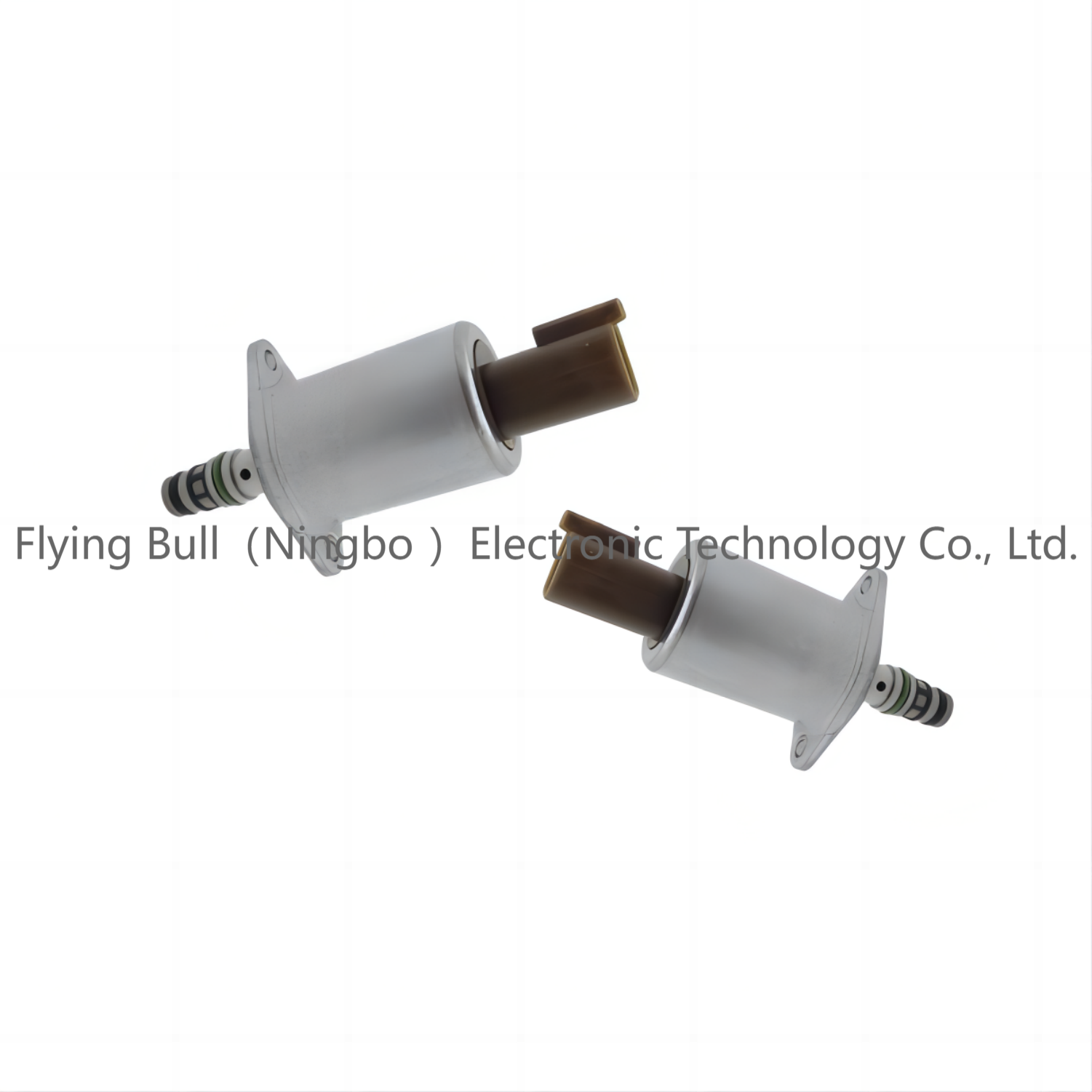
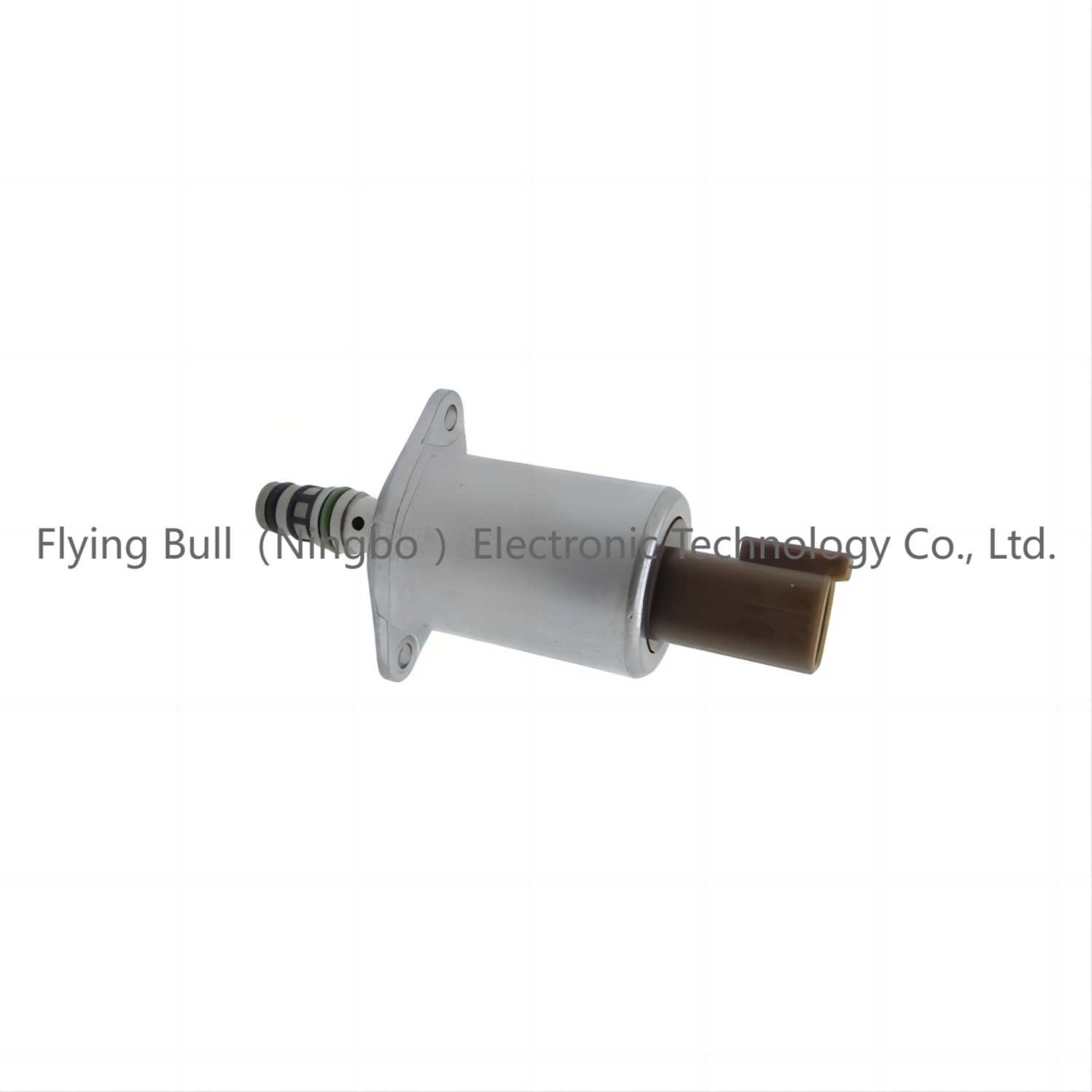



Company details








Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ