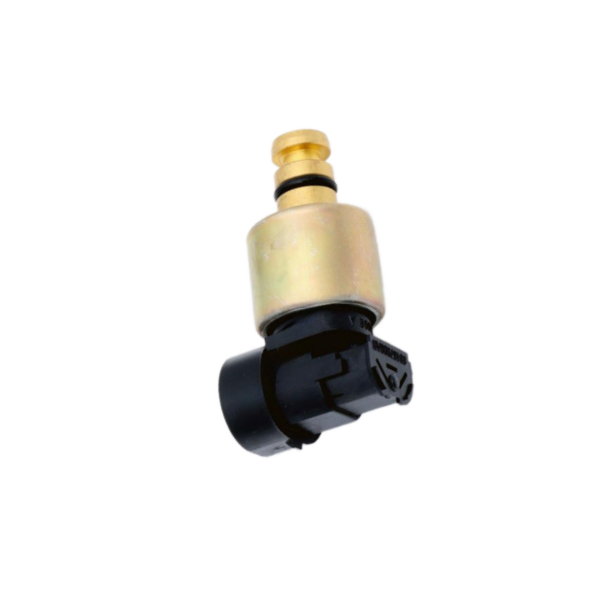
Chrysler sensor electromagnetic valve for automobile parts
Points for attention
Components of solenoid valve structure
1) Valve body:
This is the valve body to which the solenoid valve is connected. Valves are usually connected in the process pipeline to control the flow of some fluids such as liquid or air.
2) Valve inlet:
This is the port where the fluid enters the automatic valve and enters the final process from here.
3) Outlet:
Allow the fluid passing through the automatic valve to leave the valve through the outlet.
4) Coil/solenoid valve:
This is the main body of the electromagnetic coil. The main body of the solenoid coil is cylindrical and hollow from the inside. The body is covered with a steel cover and has a metal finish. There is an electromagnetic coil inside the solenoid valve.
5) Coil winding:
The solenoid consists of several turns of wires wound on ferromagnetic materials (such as steel or iron). The coil forms the shape of a hollow cylinder.
6) Leads: These are the external connections of the solenoid valve connected to the power supply. Current is supplied from these wires to the solenoid valve.
7) Plunger or piston:
This is a cylindrical solid circular metal part, which is placed in the hollow part of the solenoid valve.
8) Spring:
The plunger moves in the cavity due to the magnetic field against the spring.
9) Throttle:
Throttle is an important part of the valve, and fluid flows through it. It is the connection between the entrance and the exit.
The solenoid valve is controlled by the current passing through the coil. When the coil is energized, a magnetic field will be generated, which will cause the plunger in the coil to move. Depending on the design of the valve, the plunger will open or close the valve. When the current in the coil disappears, the valve will return to the power-off state.
In the direct-acting solenoid valve, the plunger directly opens and closes the throttle hole inside the valve. In the pilot valve (also called servo type), the plunger opens and closes the pilot hole. Inlet pressure guided through the pilot orifice opens and closes the valve seal.
The most common solenoid valve has two ports: an inlet and an outlet. Advanced designs may have three or more ports. Some designs utilize a manifold design.
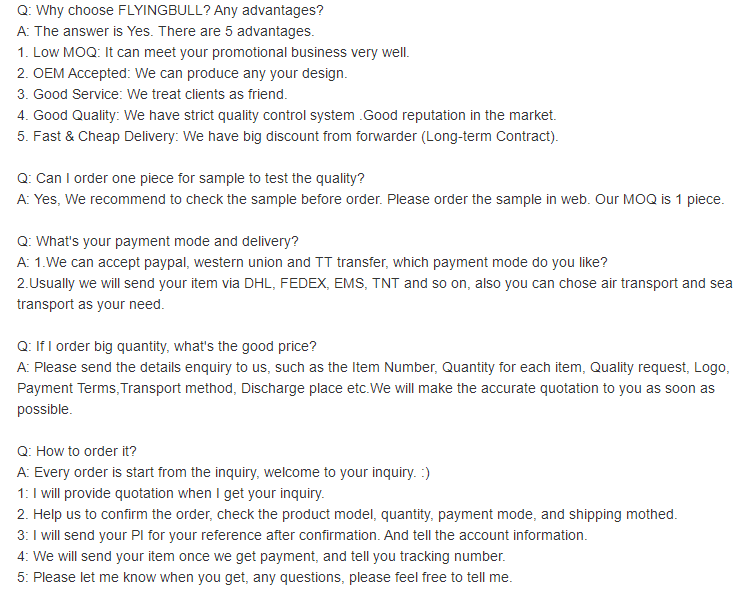
Product specification
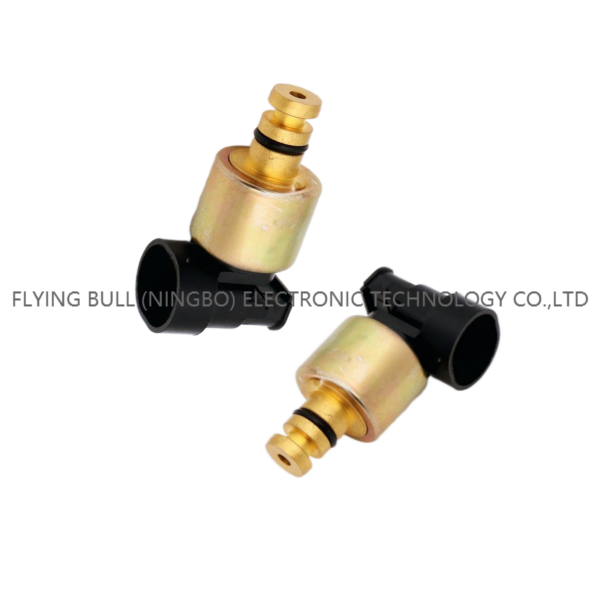

Company details
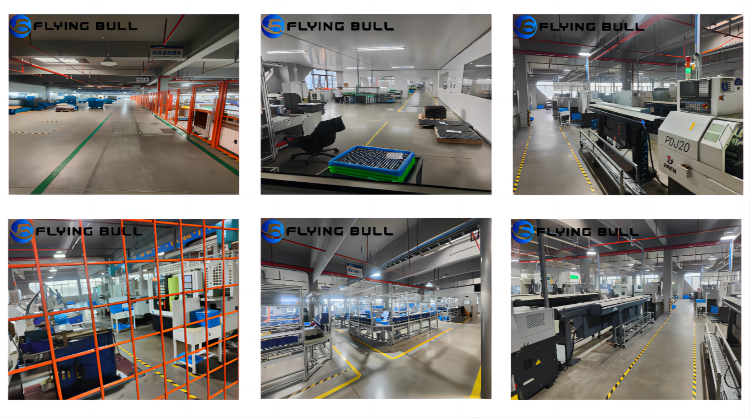







Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ