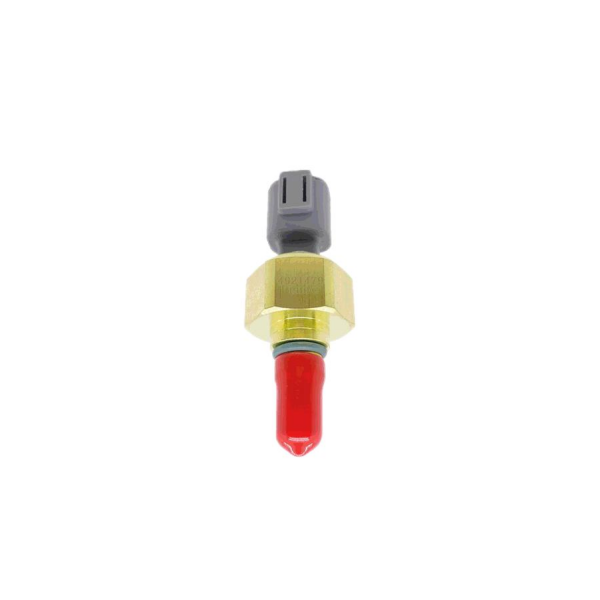
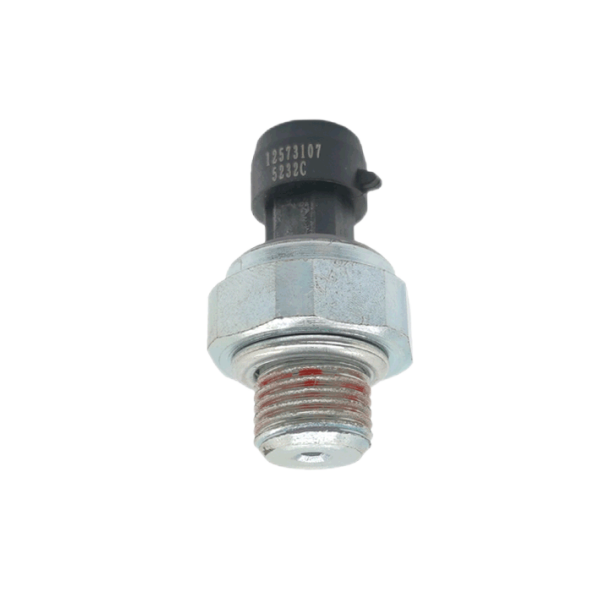
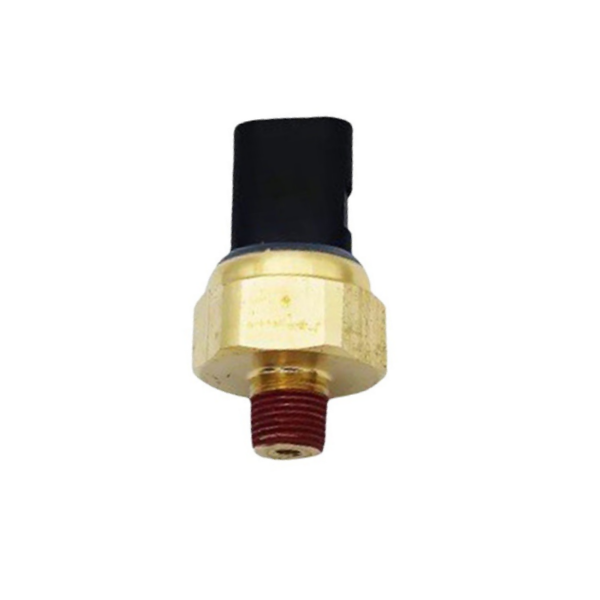
Cummins temperature and pressure sensor pressure alarm switch 4921479
Product introduction
Contactless
Its sensitive elements are not in contact with the measured object, which is also called non-contact temperature measuring instrument. This instrument can be used to measure the surface temperature of moving objects, small targets and objects with small heat capacity or rapid temperature change (transient), and can also be used to measure the temperature distribution of temperature field.
The most commonly used non-contact thermometer is based on the basic law of blackbody radiation and is called radiation thermometer. Radiation thermometry includes brightness method (see optical pyrometer), radiation method (see radiation pyrometer) and colorimetric method (see colorimetric thermometer). All kinds of radiation thermometry methods can only measure the corresponding photometric temperature, radiation temperature or colorimetric temperature. Only the temperature measured for a blackbody (an object that absorbs all radiation but does not reflect light) is the real temperature. If you want to measure the real temperature of an object, you must correct the emissivity of the material surface. However, the surface emissivity of materials depends not only on temperature and wavelength, but also on surface state, coating and microstructure, so it is difficult to measure accurately. In automatic production, it is often necessary to use radiation thermometry to measure or control the surface temperature of some objects, such as steel strip rolling temperature, roll temperature, forging temperature and the temperature of various molten metals in smelting furnace or crucible. In these specific cases, it is quite difficult to measure the emissivity of the object surface. For the automatic measurement and control of solid surface temperature, an additional reflector can be used to form a blackbody cavity with the measured surface. The influence of additional radiation can improve the effective radiation and effective emission coefficient of the measured surface. Using the effective emission coefficient, the measured temperature is corrected by the instrument, and finally the real temperature of the measured surface can be obtained. The most typical additional mirror is a hemispherical mirror. The diffuse radiation of the measured surface near the center of the ball can be reflected back to the surface by the hemispherical mirror to form additional radiation, thus improving the effective emission coefficient, where ε is the emissivity of the material surface and ρ is the reflectivity of the mirror. As for the radiation measurement of the real temperature of gas and liquid media, the method of inserting a heat-resistant material tube to a certain depth to form a blackbody cavity can be used. The effective emission coefficient of cylindrical cavity after thermal equilibrium with medium is obtained by calculation. In automatic measurement and control, this value can be used to correct the measured cavity bottom temperature (that is, the medium temperature) and get the real temperature of the medium.
Advantages of non-contact temperature measurement:
The upper limit of measurement is not limited by the temperature tolerance of temperature sensing elements, so there is no limit to the highest measurable temperature in principle. For high temperature above 1800℃, non-contact temperature measurement method is mainly used. With the development of infrared technology, radiation temperature measurement has gradually expanded from visible light to infrared light, and it has been used below 700℃ to room temperature with high resolution.
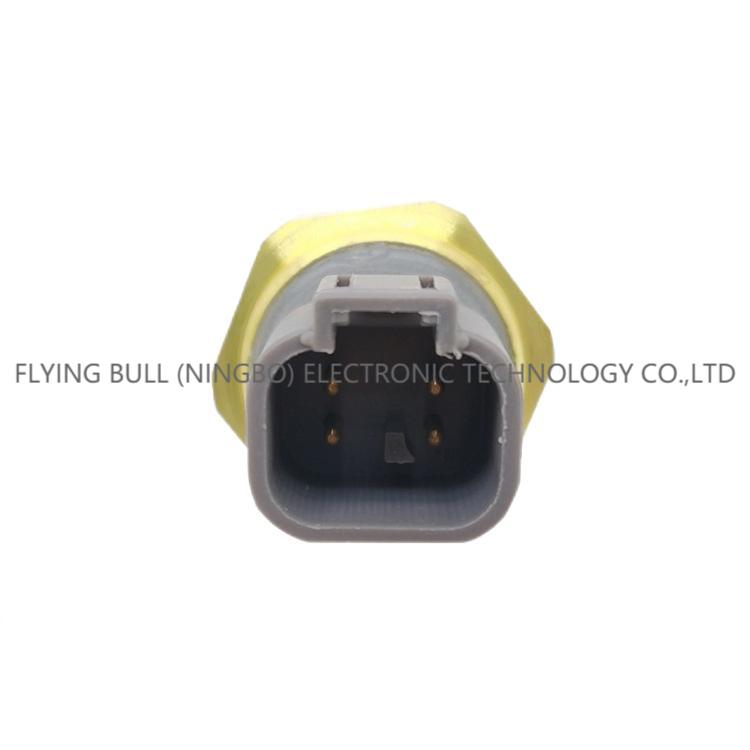
Product picture


Company details







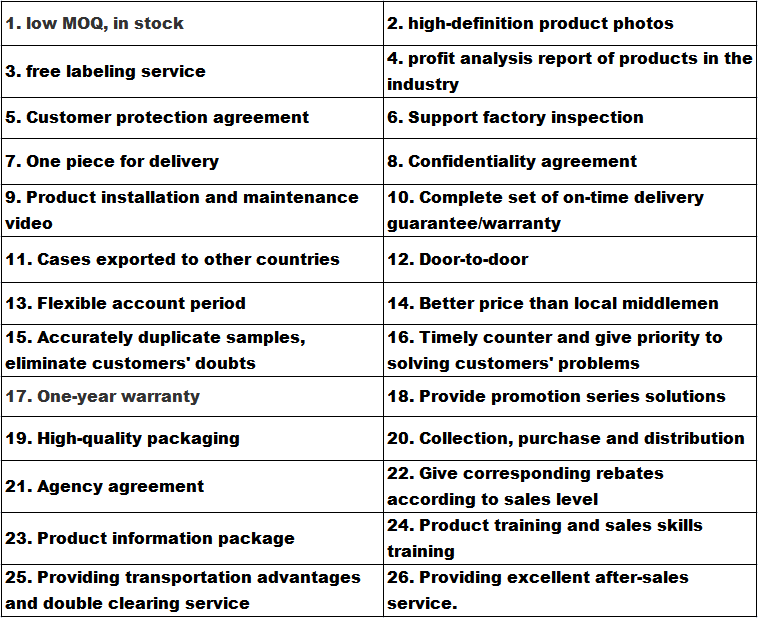
Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ














