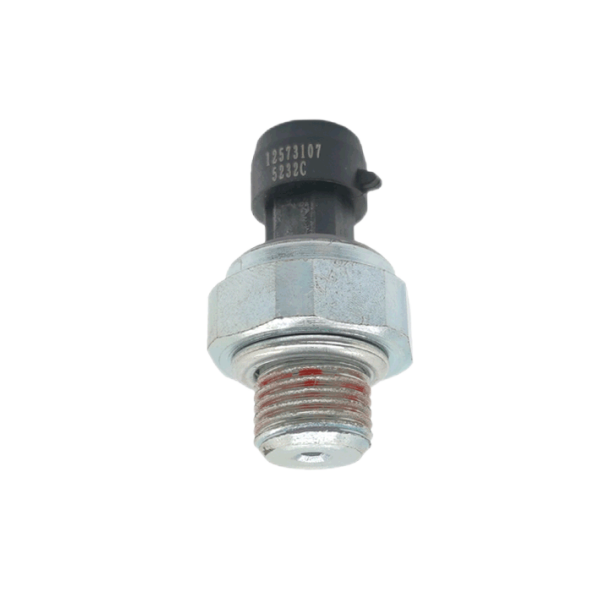
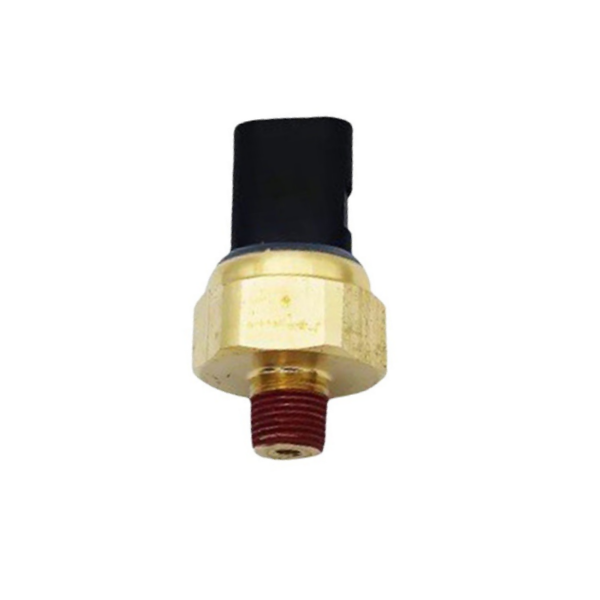
Pressure switch 97137042 is suitable for Isuzu pressure sensor
Product introduction
1. Accuracy
Accuracy is an important performance index of the sensor, which is an important link related to the measurement accuracy of the whole measurement system. The higher the accuracy of the sensor, the more expensive it is. Therefore, the accuracy of the sensor only needs to meet the accuracy requirements of the whole measurement system, and it is not necessary to choose too high. In this way, we can choose a cheaper and simpler sensor among many sensors that meet the same measurement purpose.
If the purpose of measurement is qualitative analysis, sensors with high repetition accuracy should be selected, but those with high absolute value accuracy should not be selected; If it is for quantitative analysis, it is necessary to obtain accurate measurement values, so it is necessary to choose sensors with satisfactory accuracy levels.
For some special applications, if it is impossible to choose a suitable sensor, we need to design and manufacture the sensor ourselves. The performance of the self-made sensor should meet the use requirements.
2.Kind
There are many kinds of mechanical sensors, such as resistance strain gauge pressure sensor, semiconductor strain gauge pressure sensor, piezoresistive pressure sensor, inductive pressure sensor, capacitive pressure sensor, resonant pressure sensor and capacitive acceleration sensor. But the most widely used is piezoresistive pressure sensor, which has extremely low price, high accuracy and good linear characteristics.
3.Know
When decompressing the resistive pressure sensor, we first know the resistive strain gauge. Resistance strain gauge is a kind of sensitive device that converts the strain change on the measured part into an electrical signal. It is one of the main components of piezoresistive strain sensor. Metal resistance strain gauges and semiconductor strain gauges are widely used. There are two kinds of metal resistance strain gauges: wire strain gauges and metal foil strain gauges. Usually, the strain gauge is tightly bonded to the substrate which produces mechanical strain through a special adhesive. When the stress of the substrate changes, the resistance of the strain gauge changes, so that the voltage applied to the resistor changes. Generally, this kind of strain gauge has little resistance change when it is stressed. Generally, this kind of strain gauge forms a strain bridge, which is amplified by the subsequent instrument amplifier and then transmitted to the processing circuit (usually A/D conversion and CPU) for display or execution.
Product picture

Company details
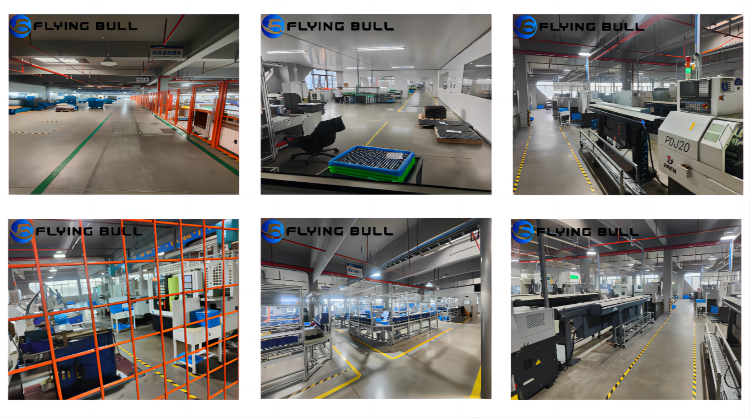







Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ














