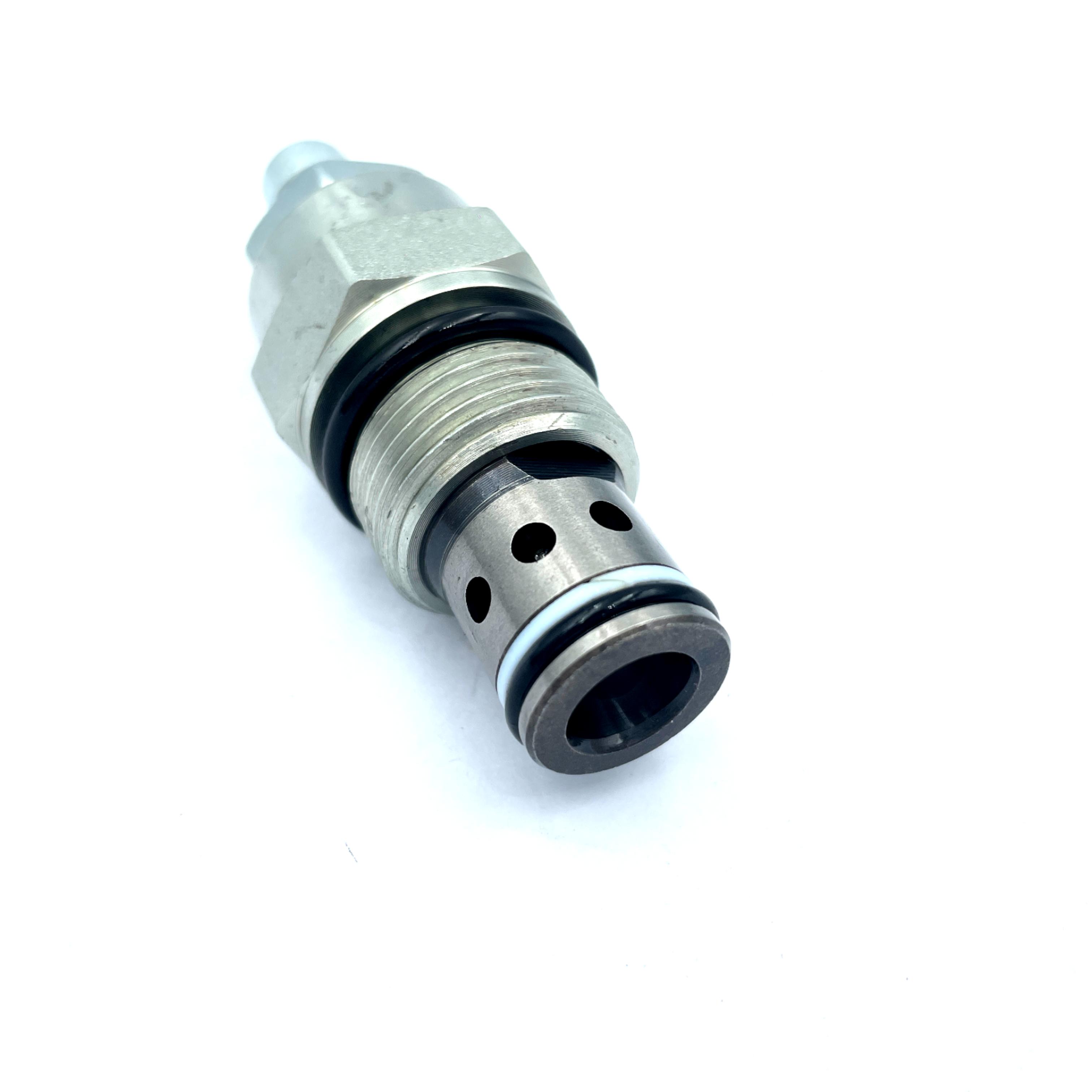
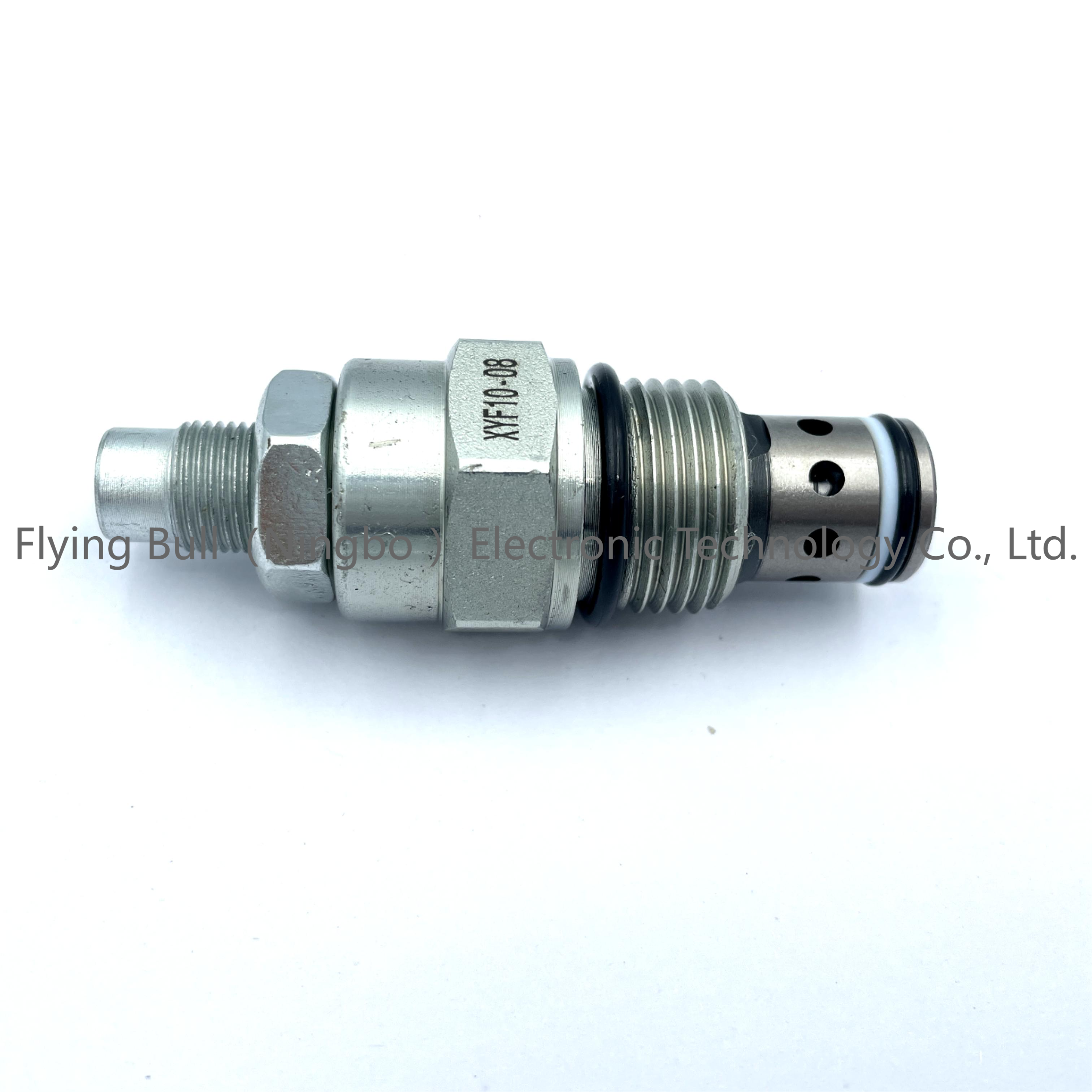
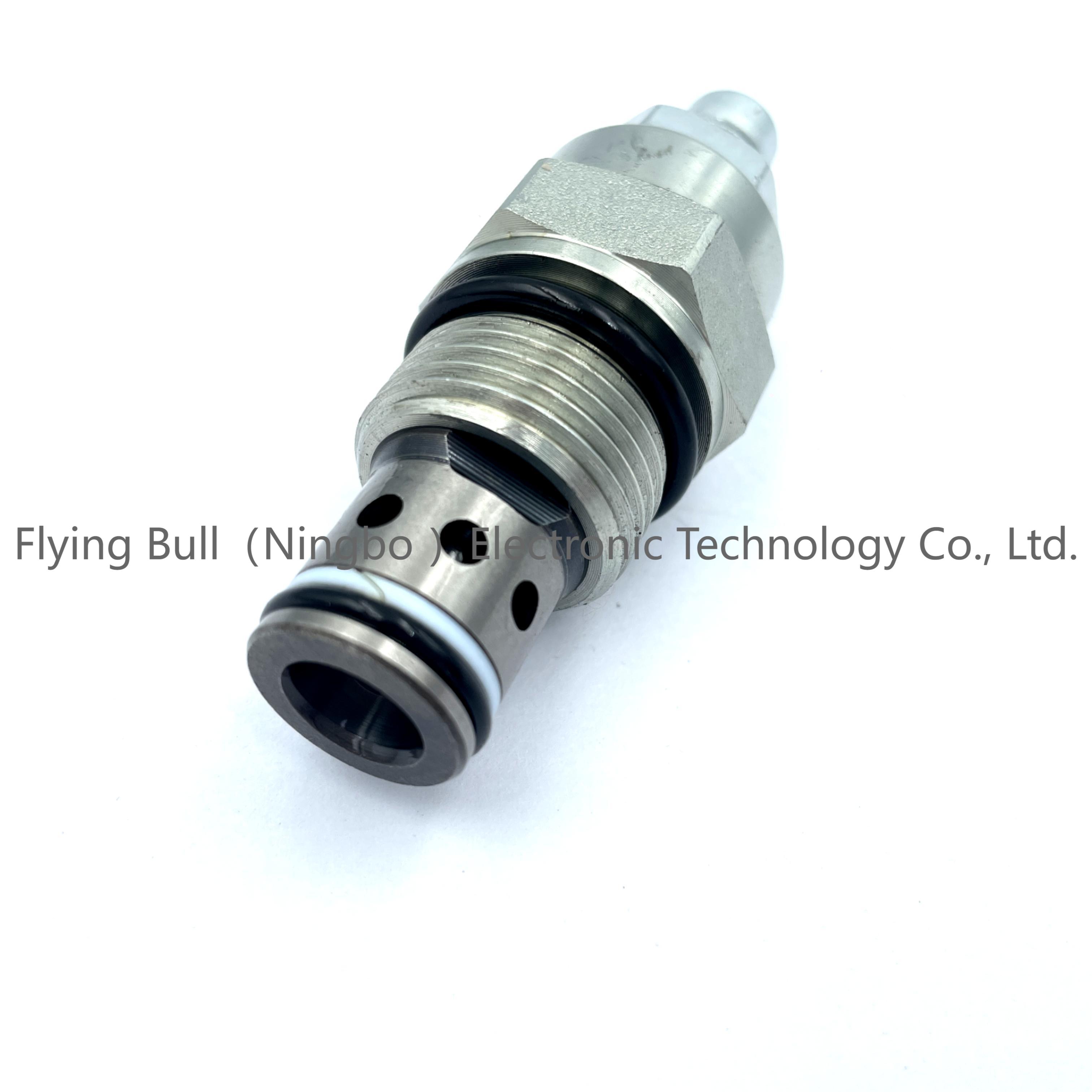
Pressure regulator Hydraulic valve Pilot operated relief valve threaded cartridge valve XYF10-08
Details
Sealing material:Direct machining of valve body
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories:valve body
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
Advantages of hydraulic system cartridge valves
Because the cartridge logic valve has been standardized at home and abroad, whether it is the international standard ISO, German DIN 24342 and our country (GB 2877 standard) have stipulated the world's common installation size, which can make the cartridge parts of different manufacturers can be interchangeable, and does not involve the internal structure of the valve, which also gives the design of the hydraulic valve has broad room for development.
The cartridge logic valve is easy to integrate: multiple components can be concentrated in a block body to form a hydraulic logic control system, which can reduce the weight of the system composed of conventional pressure, direction and flow valves by 1/3 to 1/4, and the efficiency can be increased by 2% to 4%.
Fast reaction speed: Because the cartridge valve is a seat valve structure, the spool starts to pass oil as soon as it leaves the seat. On the contrary, the slide valve structure must finish the covering amount before starting to connect the oil circuit, and the time to complete the pressure relief of the control chamber and open the cartridge valve is only about 10ms, and the reaction speed is fast.
Principle of direct-acting solenoid valve: When energized, the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnetic coil lifts the closing part from the seat, and the valve opens; When the power is off, the electromagnetic force disappears, the spring presses the closing part on the seat, and the valve is closed.
Step by step direct acting solenoid valve principle: it is a combination of direct acting and pilot principle, when there is no pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet, after the power, the electromagnetic force directly to the pilot small valve and the main valve closing parts lift up in turn, the valve opens. When the inlet and outlet reach the starting pressure difference, after power, the electromagnetic force pilot small valve, the main valve lower chamber pressure rises, the upper chamber pressure drops, so as to use the pressure difference to push the main valve upward; When the power is off, the pilot valve uses spring force or medium pressure to push the closing part and moves downward to close the valve.
Pilot solenoid valve principle: when powered on, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole, the upper chamber pressure drops rapidly, forming a low and high pressure difference around the closing part, the fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move upward, the valve opens; When the power is off, the spring force closes the pilot hole, and the inlet pressure forms a low and high pressure difference around the valve closing part through the bypass hole rapidly, and the fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move down and close the valve.
Product specification
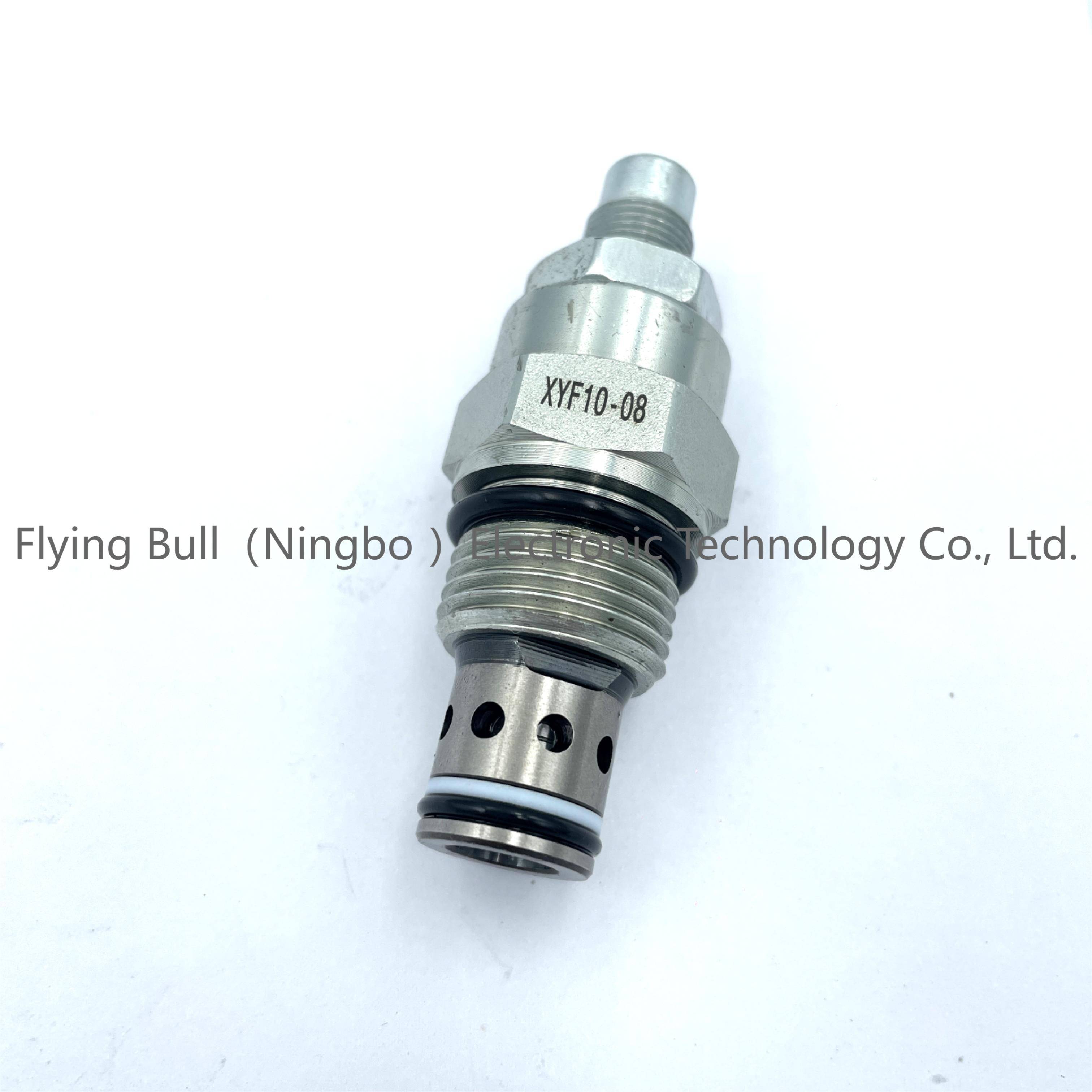



Company details







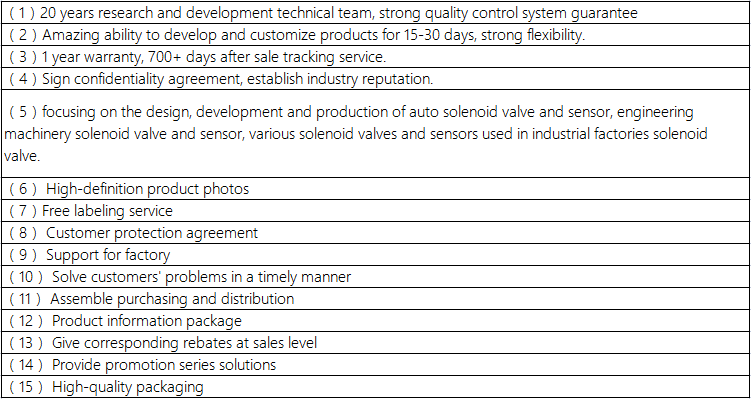
Company advantage
Transportation

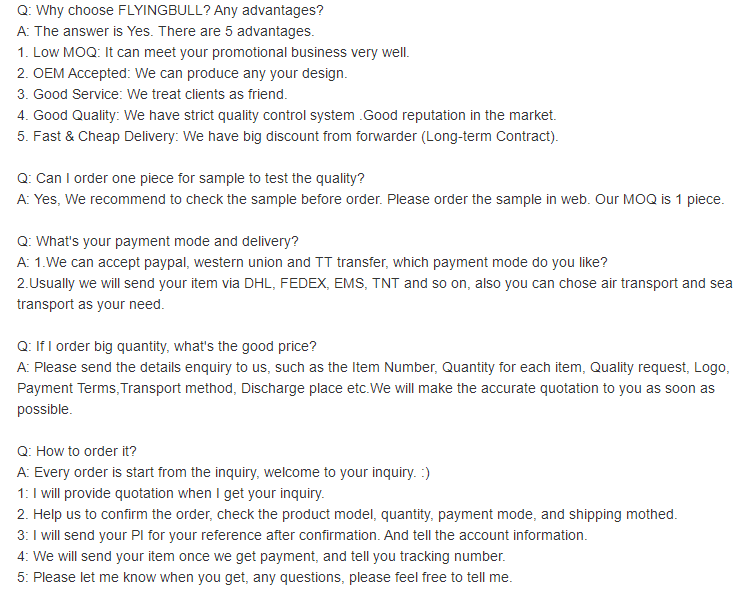
FAQ