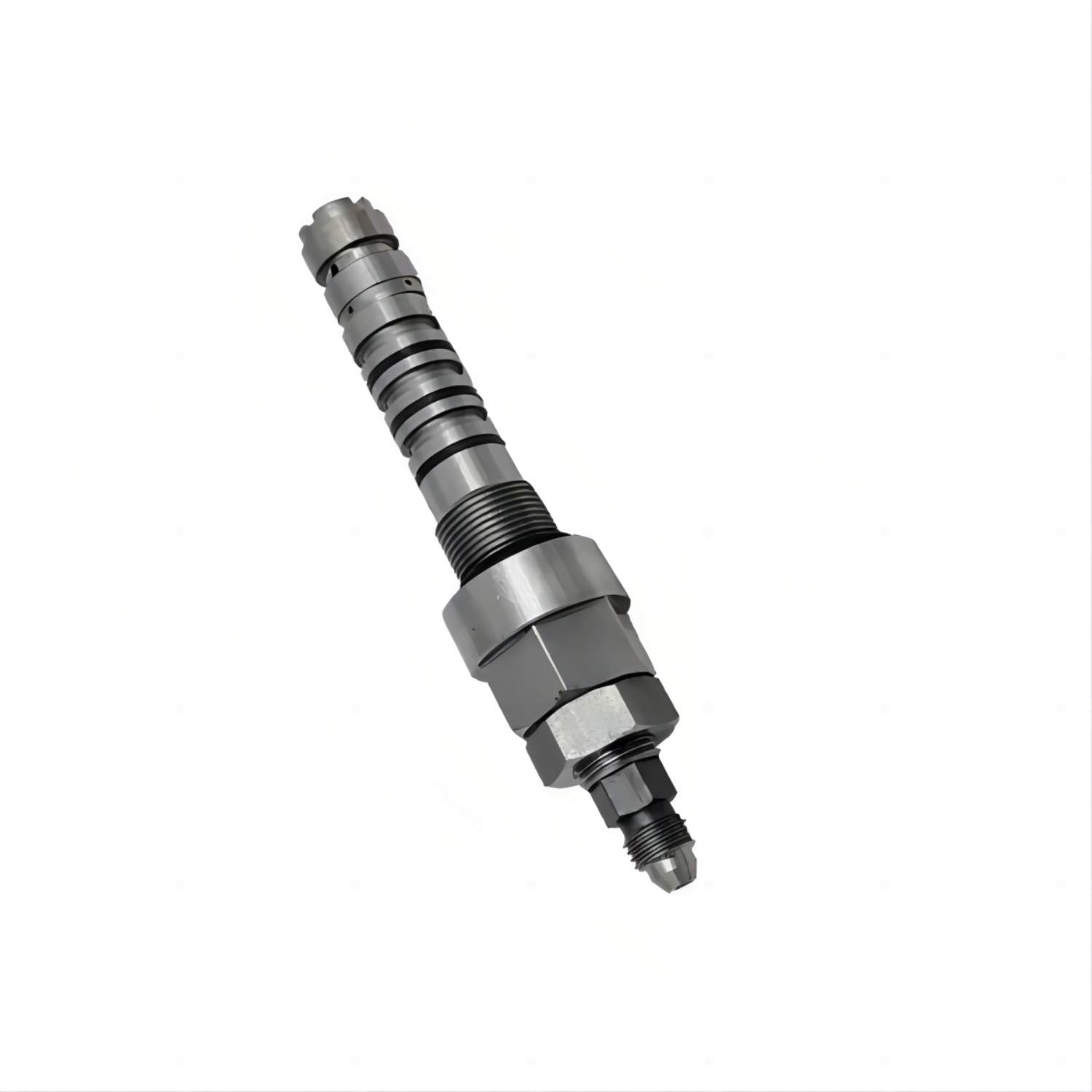
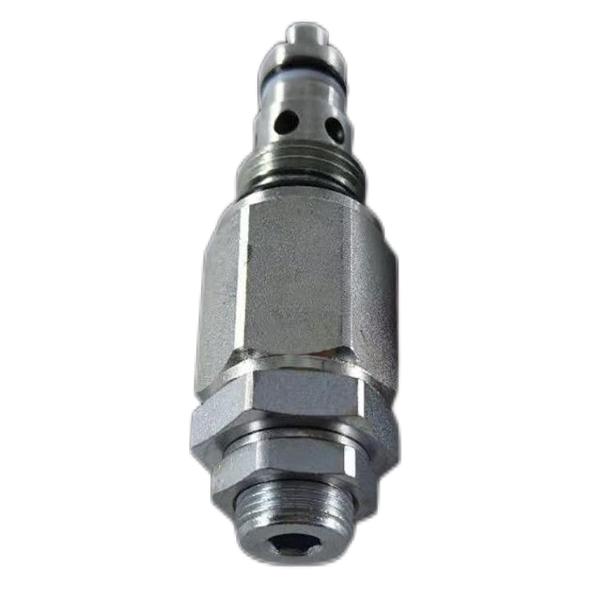
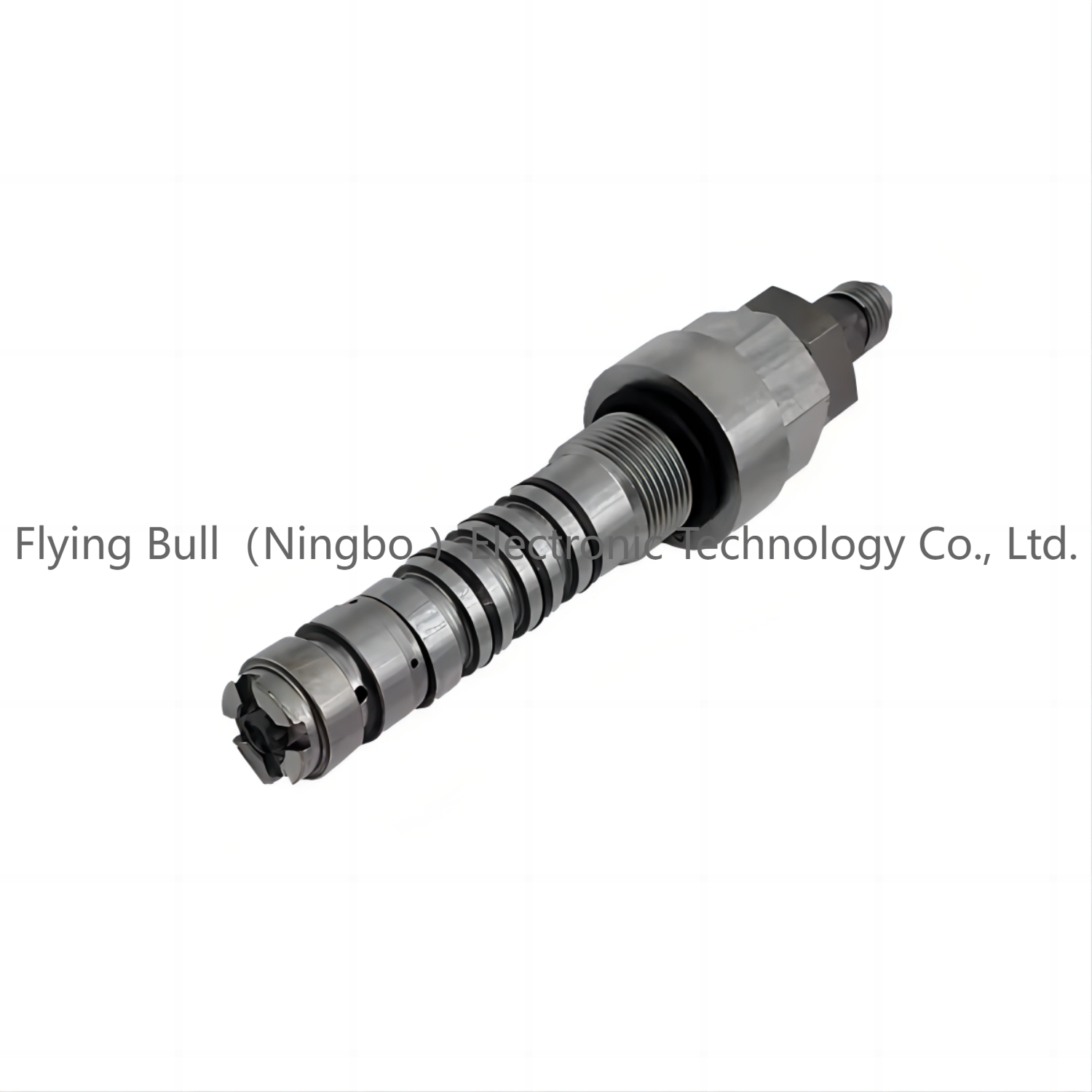
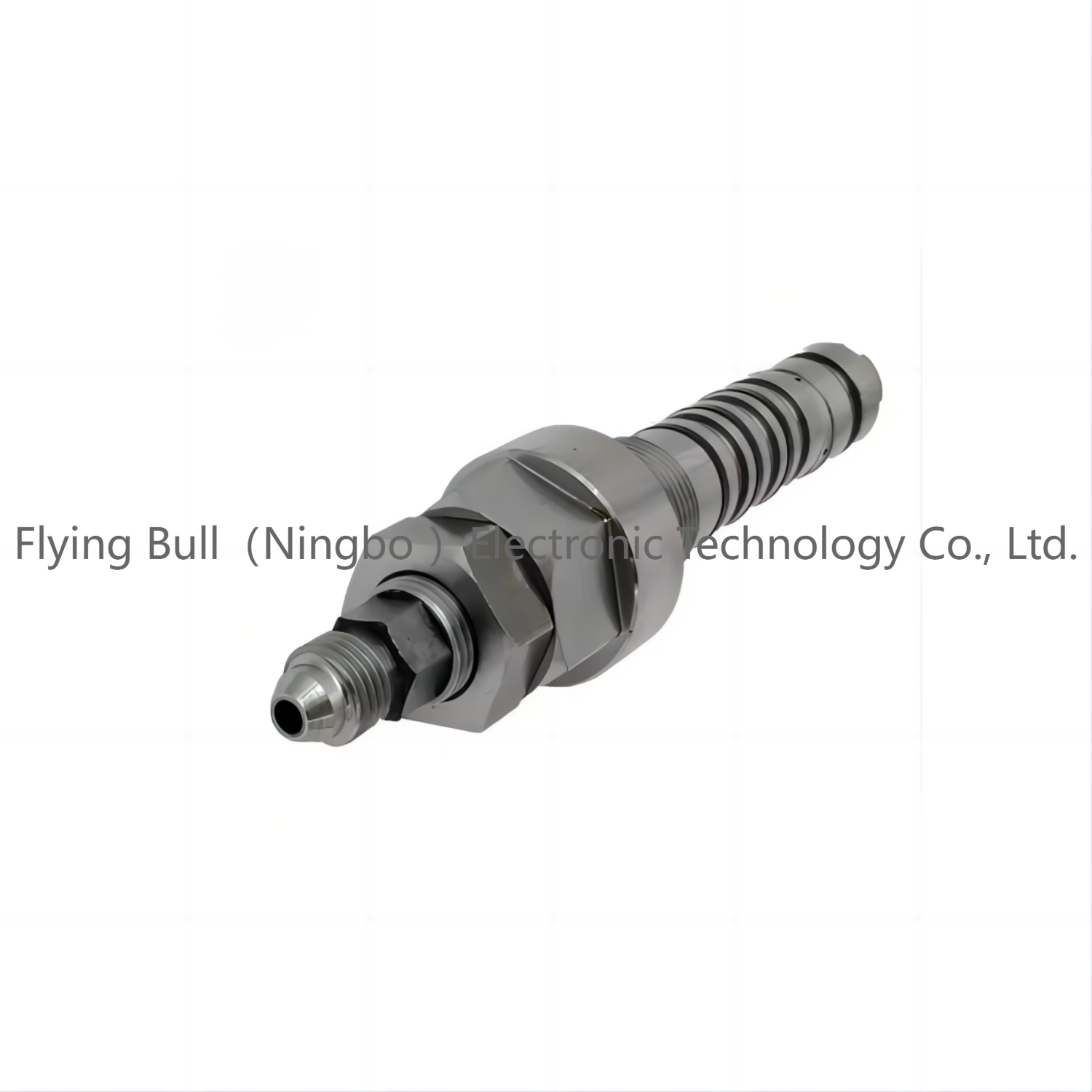
PC200-6 Relief valve PC220-6 Excavator safety valve 708-1L-04720
Details
Warranty:1 Year
Brand Name:Flying Bull
Place of Origin:Zhejiang, China
Valve type:Hydraulic valve
Material body:carbon steel
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Applicable industries:machinery
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
Proportional solenoid valve
The proportional solenoid valve generally regulates the opening of the valve through an external voltage signal, and is commonly used to regulate the flow of fluid through the valve.
Electrical proportional valves are generally used to regulate and control the fluid outlet pressure, which is an important difference between them, one is to regulate the flow, the other is to regulate and control the pressure.
The composition of the electrical proportional valve is generally composed of two proportional solenoid valves, pressure sensors and controllers, a proportional valve controls the inlet flow, another proportional valve controls the outlet flow, the sensor measures the pressure, and the controller controls the opening of the two proportional valves through feedback signals, so that the pressure in the middle chamber (also equal to the outlet pressure) is equal to the set value.
1. Principle of direct-acting solenoid valve: When energized, the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnetic coil lifts the closing part from the seat, and the valve opens; When the power is off, the electromagnetic force disappears, the spring presses the closing part on the seat, and the valve is closed.
2, step by step direct acting solenoid valve principle: it is a combination of direct acting and pilot principle, when there is no pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet, after the power, the electromagnetic force directly to the pilot small valve and the main valve closing parts lift up in turn, the valve opens. When the inlet and outlet reach the starting pressure difference, after power, the electromagnetic force pilot small valve, the main valve lower chamber pressure rises, the upper chamber pressure drops, so as to use the pressure difference to push the main valve upward; When the power is off, the pilot valve uses spring force or medium pressure to push the closing part and moves downward to close the valve.
3, pilot solenoid valve principle: when powered on, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole, the upper chamber pressure drops rapidly, forming a low and high pressure difference around the closing part, the fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move upward, the valve opens; When the power is off, the spring force closes the pilot hole, and the inlet pressure forms a low and high pressure difference around the valve closing part through the bypass hole rapidly, and the fluid pressure pushes the closing part to move down and close the valve.
Product specification
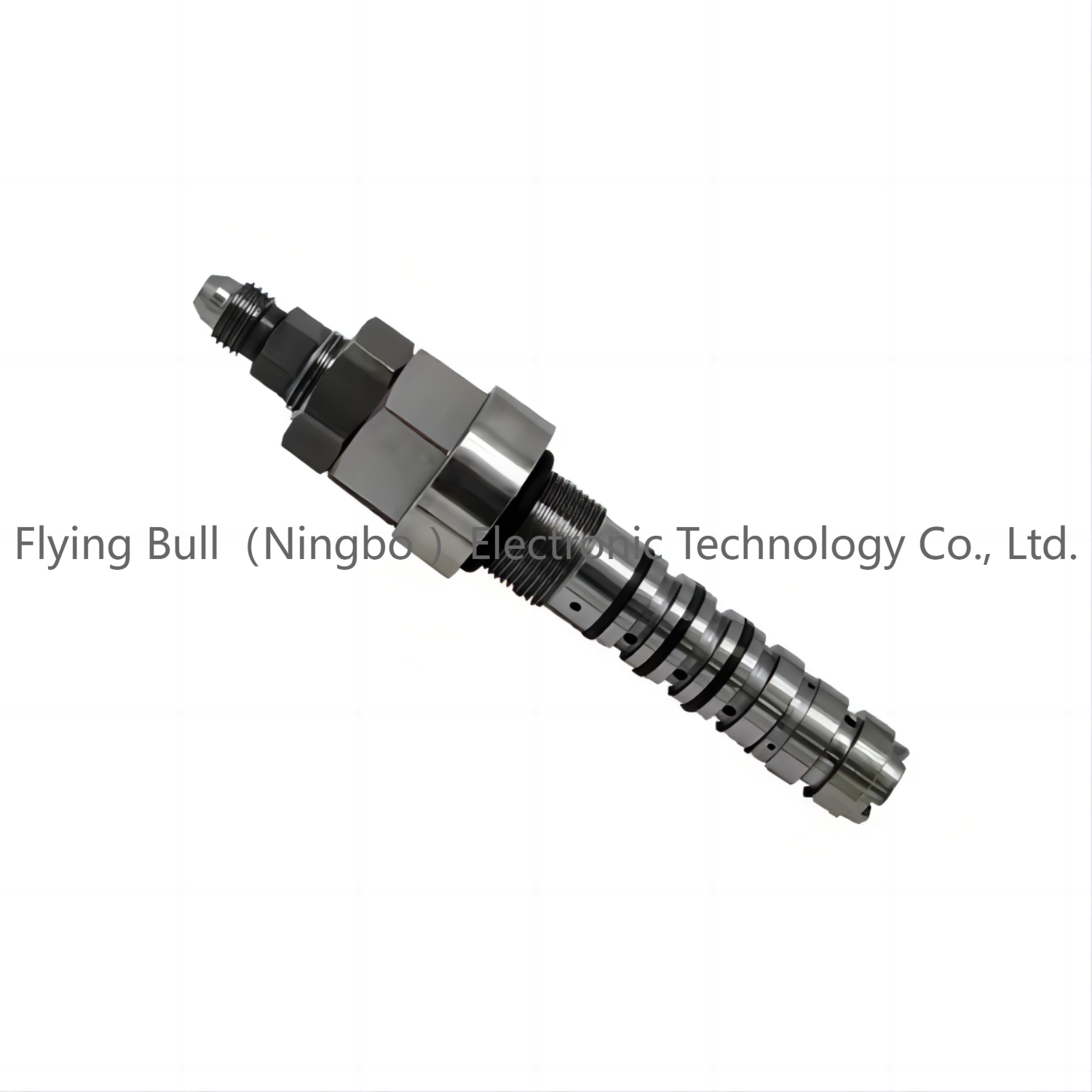



Company details







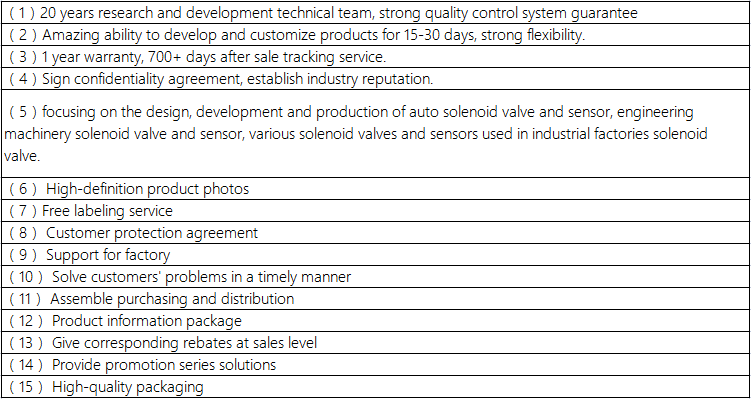
Company advantage
Transportation

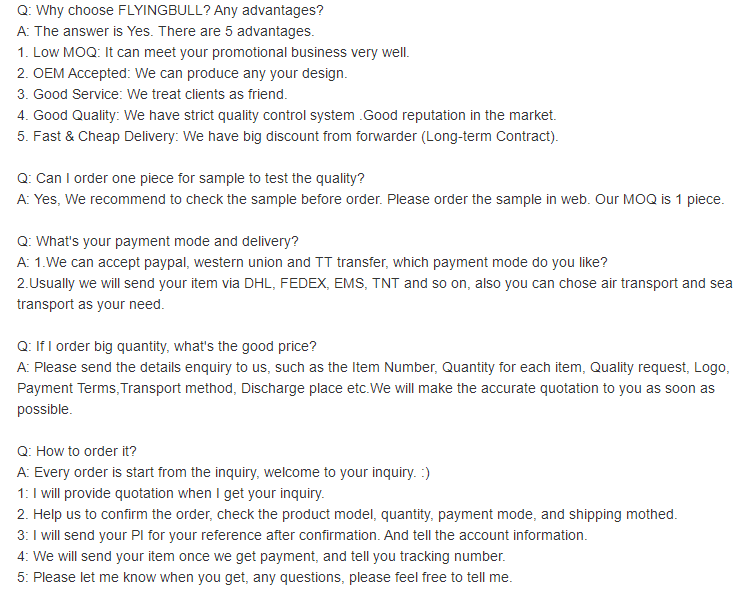
FAQ