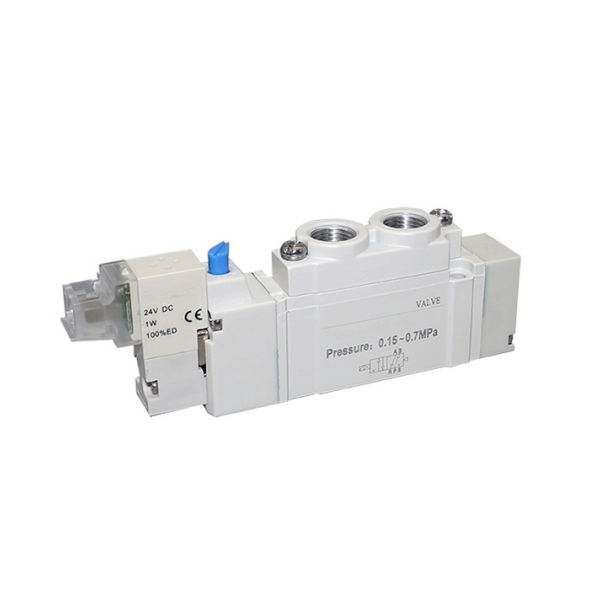
Two-position five-way solenoid valve with low power consumption
Product introduction
In the process of industrial production in China, large-scale mechanical automation has been realized, and in the process of mechanical automation operation, the improvement and innovation of each component plays an important role in promoting the whole production process.
1. Electromagnetic directional valve is a common device in construction machinery, which has many types and can be installed in different positions according to the different requirements of control system.
Because the overall structure is relatively simple, the cost is relatively low, and the operation and maintenance are relatively convenient, the application field is relatively wide. The working principle of electromagnetic directional valve is relatively simple, which mainly controls the direction, flow, speed and other parameters of fluid through electromagnetism. It has strong sensitivity and accuracy and can adapt to the needs of various operating environments.
2. Working principle of electromagnetic directional valve Although there are many types of electromagnetic directional valves, their working principles are basically the same.
The electromagnetic directional valve is mainly composed of valve body, valve core, spring, armature and electromagnetic coil. After the electromagnet is energized, the parameters such as direction, flow rate and speed of fluid media such as gas and liquid can be controlled. The working principle of electromagnetic directional valve is relatively simple. There is a closed cavity in the valve body. According to the actual needs, holes will be opened at different positions of the cavity to communicate with the outside, and each hole will be connected with the corresponding pipeline. Install the valve core in the middle of the cavity, which will be integrated with the armature, and install an electromagnet and a spring on both sides. On which side of the magnet coil is energized, a certain electromagnetic force will be generated. When this electromagnetic force exceeds the elastic force of the spring, the valve core will be attracted to control the opening or closing of the external hole through the movement of the valve core. During the power-on and power-off of the solenoid, the spool will move left and right, and the spring will play a certain buffering role during the movement to avoid the spool from generating too much impact on the valve body.
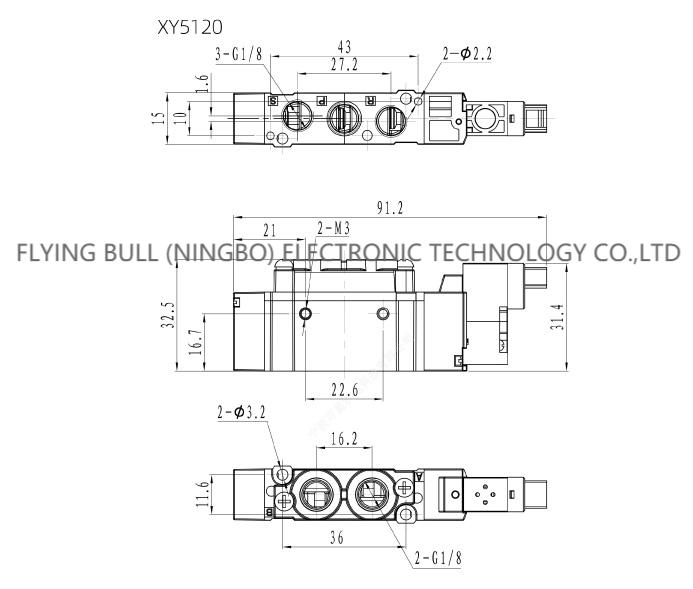
Product picture
Company details







Company advantage

Transportation

FAQ









