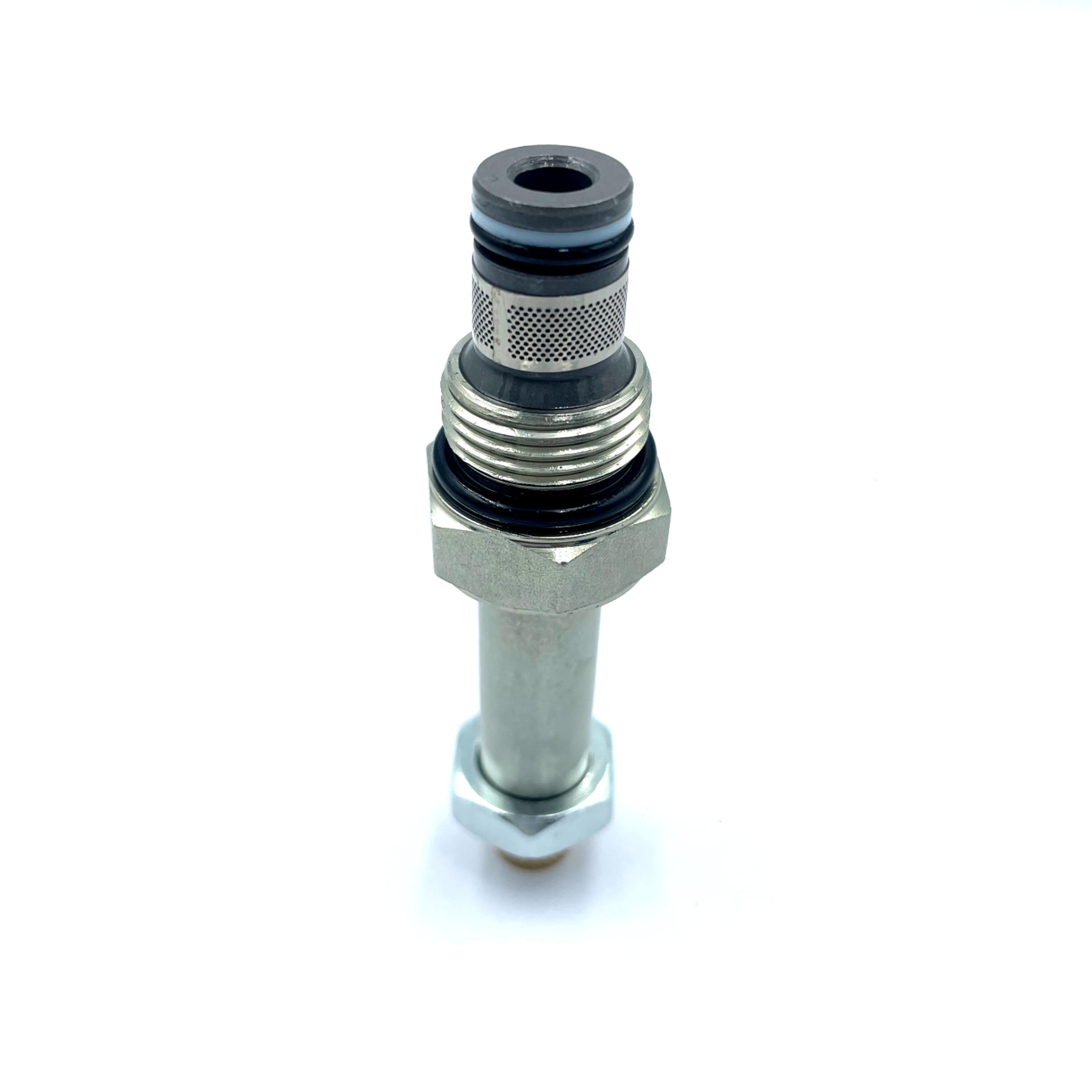
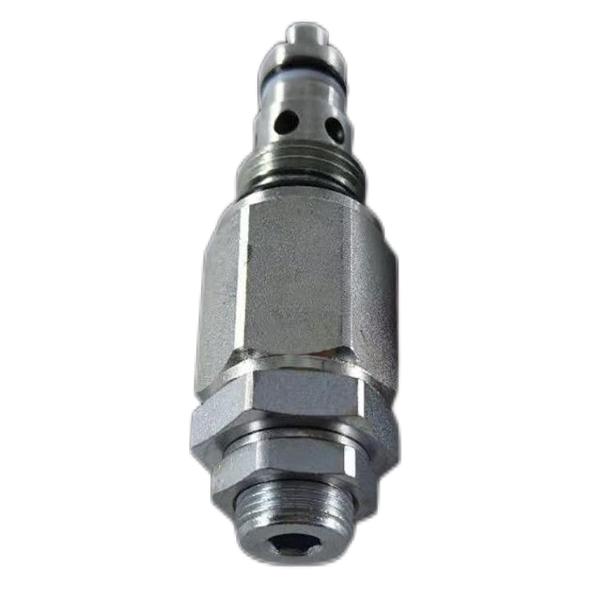
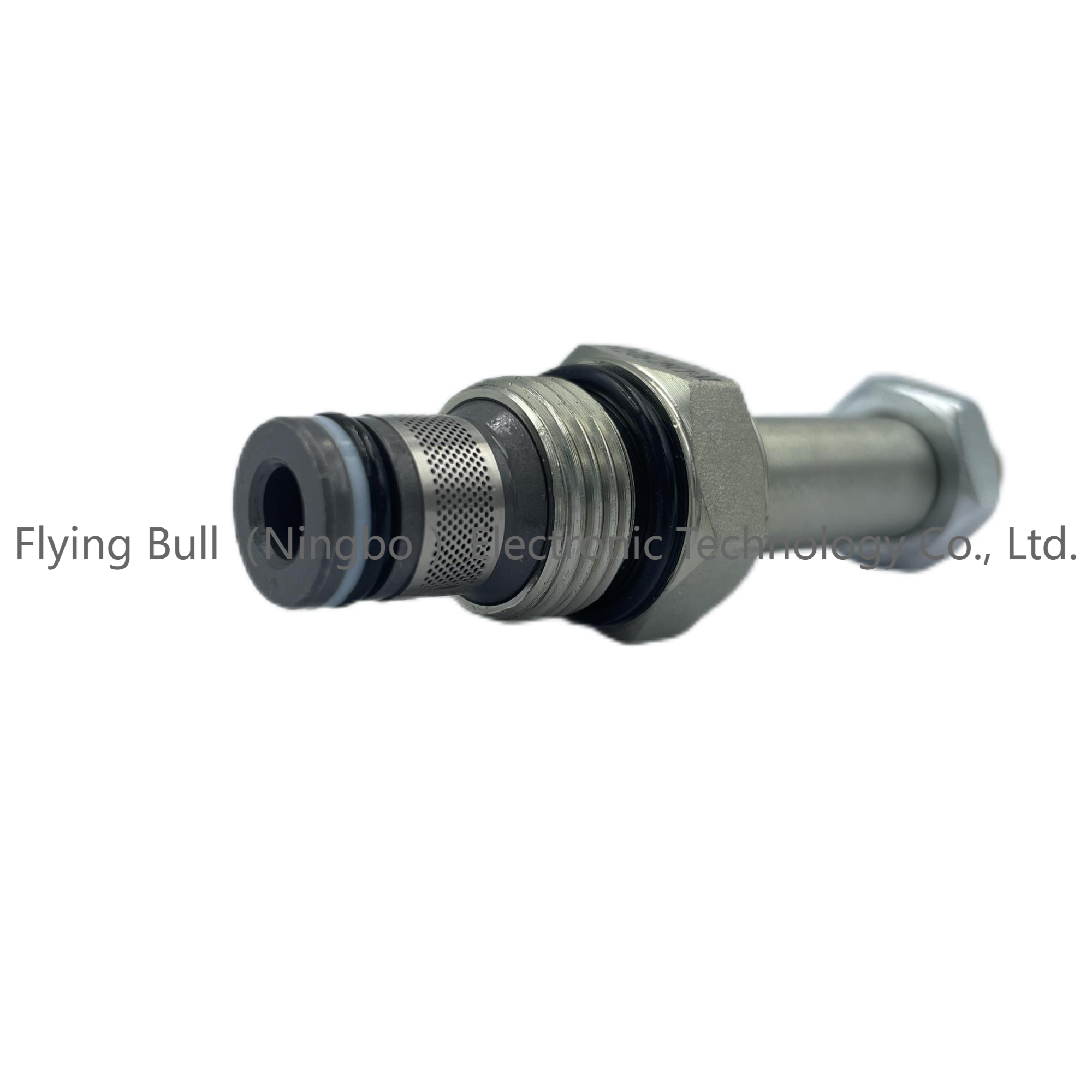
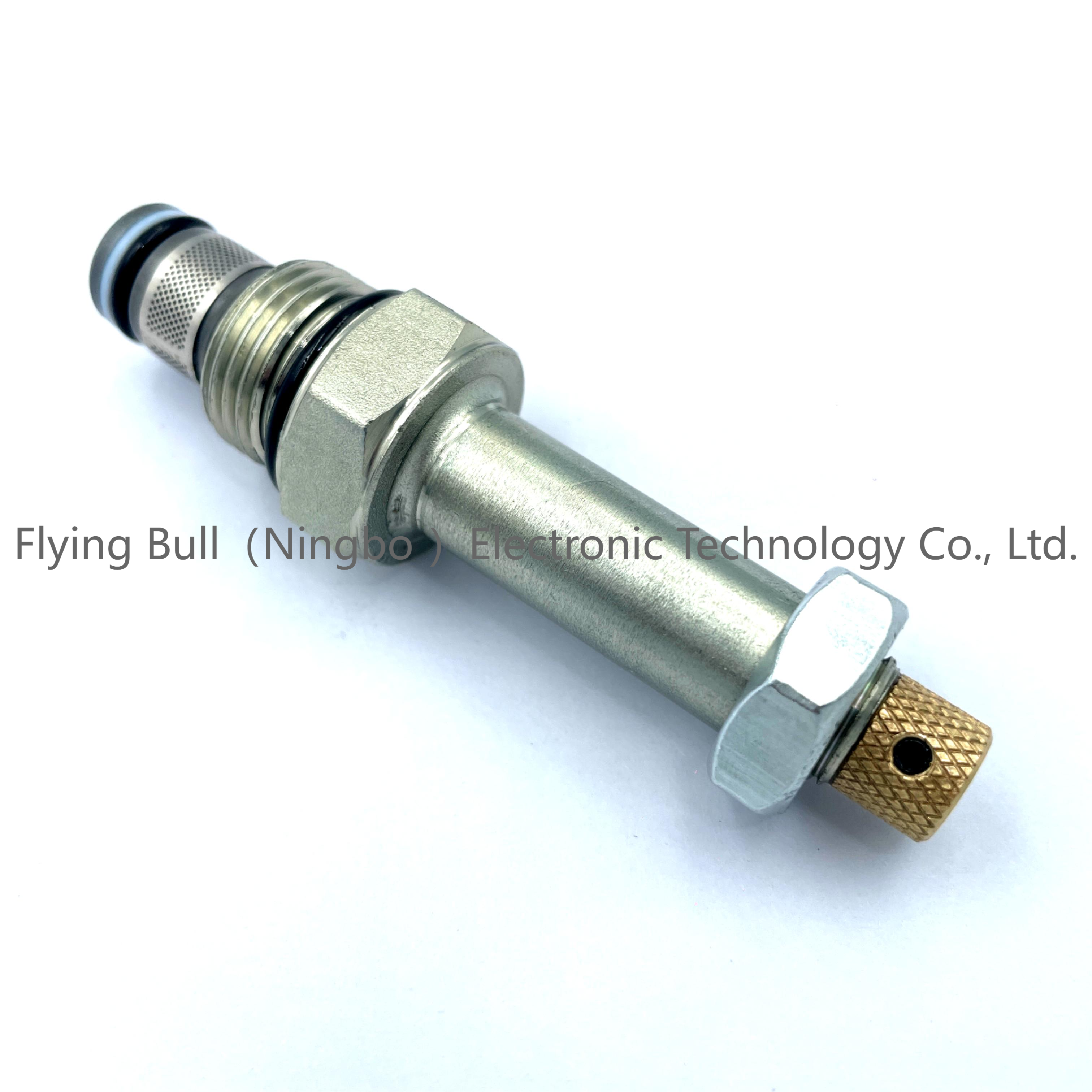
Double check solenoid valve SV2-08-2NCP-M threaded cartridge valve Hydraulic valve
Details
Sealing material:Direct machining of valve body
Pressure environment:ordinary pressure
Temperature environment:one
Optional accessories:valve body
Type of drive:power-driven
Applicable medium:petroleum products
Points for attention
All kinds of threaded cartridge valves: structure, working principle and performance
Cartridge valves can be divided into two types of installation: Slip-in and Screw-in
Class. The slip-in type is usually called a two-way cartridge valve or logic element, which generally requires additional pilot control valves to work
Do. The screw type is the threaded cartridge valve described in this article, which can generally complete one or more independently (after loading the mounting hole)
Hydraulic functions, such as relief valve, electromagnetic direction valve, flow control valve, balance valve, etc.
Application of threaded cartridge valve
The biggest feature of threaded cartridge valve is flexible application.
It can be installed separately with a single valve block or a double valve block (valve suppliers can generally provide such valve blocks at the same time)
It is a tubular element.
It can also be installed in the hydraulic motor, hydraulic pump body, or hydraulic cylinder interface, as a control valve.
It can also be fitted into a valve block with a CETOP interface as a vertical stack valve or a transverse sheet assembly valve.
It can also be installed in the control cover plate of the two-way cartridge valve as pilot control.
Finally, it can also be fitted with a specially designed (pure) threaded cartridge valve assembly block,
Structure and performance characteristics of threaded cartridge valve
As shown in the figure, a two-way threaded cartridge type direct-acting relief valve plug-in of a typical structure is screwed into the two-way valve hole as shown in Figure 2a. The inlet and outlet 2 and the system are connected through the holes in the cartridge valve block. A sealing ring is installed on the plug-in. The plug-in can also be inserted into a standard plate valve body with a threaded orifice or a body with a standard oil thread to form a discrete plate or threaded valve. This is especially necessary for the test of threaded cartridge valves.
In addition to the above two holes, there are three and four holes, and the new two way cartridge valve field has only two holes. The former is more simple, flexible and compact in forming various types of pressure, flow and direction valves. As shown in Figure 4, the new one-thread plug-in requires four plug-ins, as shown in Figure 5. Obviously the latter is bigger and more expensive.
Product specification



Company details







Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ