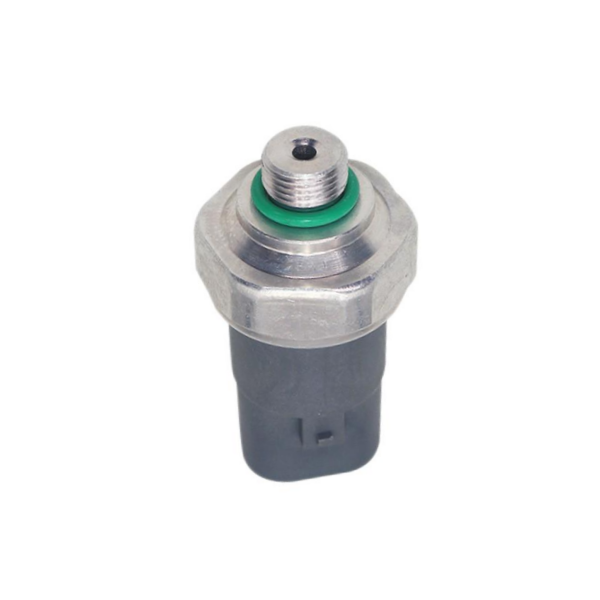
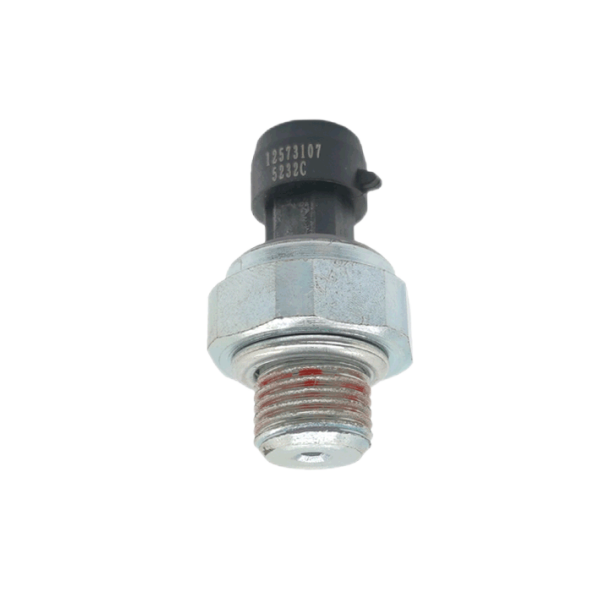
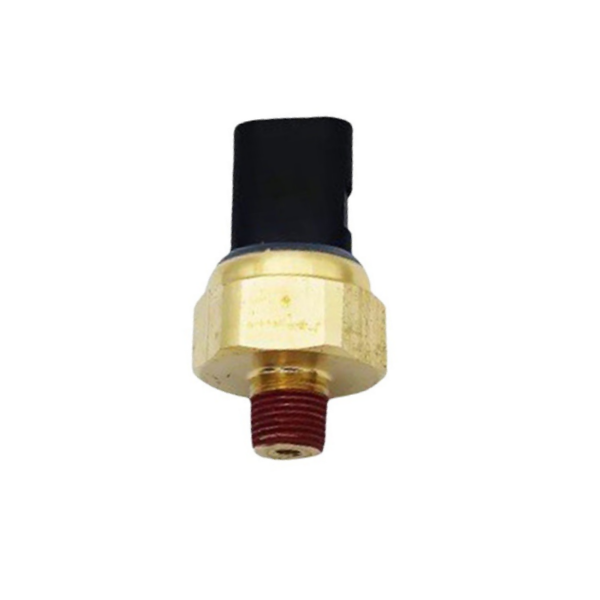
Suitable for Toyota switch pressure sensor 88645-60030
Product introduction
The technology used by current sensors is very important, because different sensors may have different characteristics for various applications. Most sensors can work because current-carrying wires will generate magnetic fields. When directly measuring the current in the circuit, please use the current detection resistor.
1. Hall effect-Hall effect sensor consists of core, Hall effect device and signal conditioning circuit. The sensor works when the current conductor passes through the magnetic core which concentrates the magnetic field of the conductor. Hall effect devices installed in a magnetic core at right angles to a concentrated magnetic field excite hall element with a constant current (in one plane). Then, the energized hall element is exposed to the magnetic field from the core, and a potential difference is generated, which can be measured and amplified as a process-level signal, such as 4-20mA or contact closure.
2. Inductive-inductive sensors use coils through which current-carrying wires pass. This causes a current proportional to the current to flow into the coil. This is because of the magnetic field generated by the flowing current. Inductive sensors are used for alternating current. The sensor has a winding core and a signal conditioner. When the current conductor passes through the magnetic core, it will be amplified by the magnetic field of the conductor. Because alternating current constantly changes from negative potential to positive potential (usually 50 to 60 Hz), it will produce an expanding and contracting magnetic field, so current will be induced in the winding. The proces of converting that secondary current into voltage and stabilize the output; Signal, such as 4-20mA or contact closure.
3. Magnetoresistance-Magnetoresistance effect is a characteristic of some materials, and its resistance value can be changed according to the applied magnetic field. If no magnetic flux is applied, the current will flow directly through the plate. If a magnetic flux is applied, the Lorentz force proportional to the magnetic flux density will deflect the current path. With the deflection of the current path, the distance of current flowing through the plate becomes longer, which leads to the increase of resistance.
Product picture

Company details
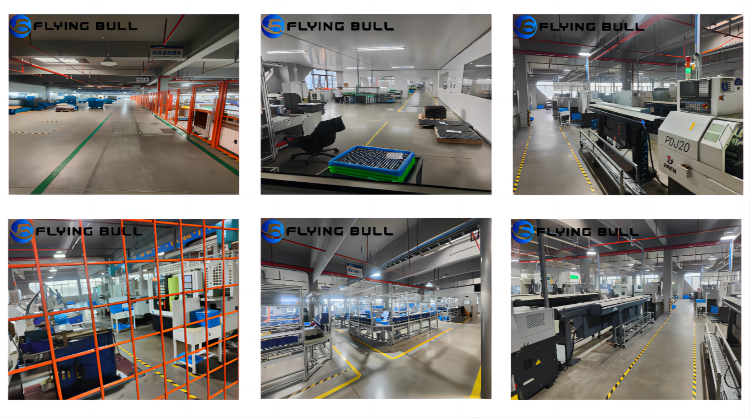







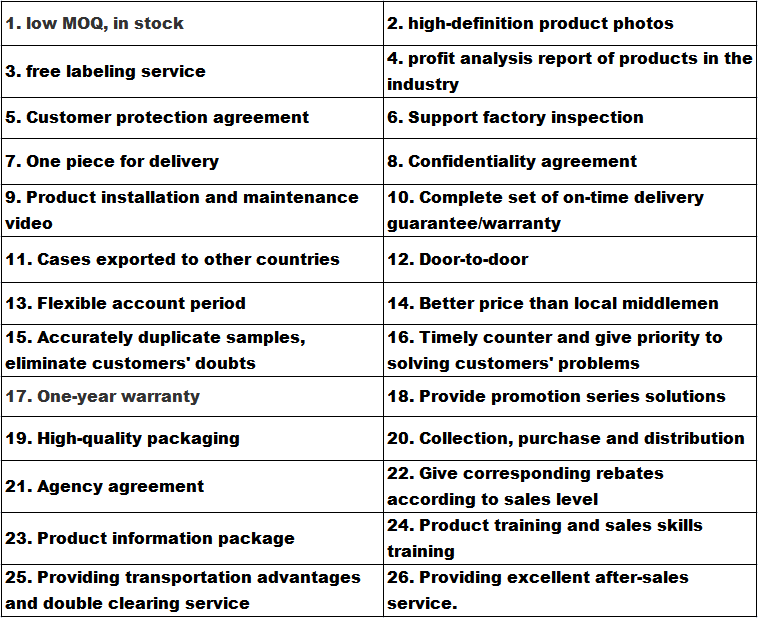
Company advantage
Transportation

FAQ














